Genetic and molecular interactions between BELL1 and MADS box factors support ovule development in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 17693535
- PMCID: PMC2002616
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.107.051797
Genetic and molecular interactions between BELL1 and MADS box factors support ovule development in Arabidopsis
Abstract
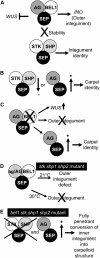
In Arabidopsis thaliana and many other plant species, ovules arise from carpel tissue as new meristematic formations. Cell fate in proliferating ovule primordia is specified by particular ovule identity factors, such as the homeodomain factor BELL1 (BEL1) and MADS box family members SEEDSTICK (STK), SHATTERPROOF1 (SHP1), SHP2, and AGAMOUS. Both in the bel1 mutant and the stk shp1 shp2 triple mutant, integuments are transformed into carpelloid structures. Combining these mutants in a bel1 stk shp1 shp2 quadruple mutant, we showed that the bel1 phenotype is significantly enhanced. We also demonstrate that ovule differentiation requires the regulation of the stem cell maintenance gene WUSCHEL, repression of which is predominantly maintained by BEL1 during ovule development. Based on yeast three-hybrid assays and genetic data, we show that BEL1 interacts with the ovule identity MADS box factors when they dimerize with SEPALLATA proteins. We propose a model for ovule development that explains how the balance between carpel identity activity and ovule identity activity is established by a MADS box homeodomain protein complex.
Figures




References
-
- Alvarez, J., and Smyth, D.R. (1999). CRABS CLAW and SPATULA, two Arabidopsis genes that control carpel development in parallel with AGAMOUS. Development 126 2377–2386. - PubMed
-
- Balasubramanian, S., and Schneitz, K. (2002). NOZZLE links proximal-distal and adaxial-abaxial pattern formation during ovule development in Arabidopsis thaliana. Development 129 4291–4300. - PubMed
-
- Battaglia, R., Brambilla, V., Colombo, L., Stuitje, A.R., and Kater, M.M. (2006). Functional analysis of MADS-box genes controlling ovule development in Arabidopsis using the ethanol-inducible alc gene-expression system. Mech. Dev. 123 267–276. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

