In vivo hexamerization and characterization of the Arabidopsis AAA ATPase CDC48A complex using forster resonance energy transfer-fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy and fluorescence correlation spectroscopy
- PMID: 17693538
- PMCID: PMC2048723
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.107.103986
In vivo hexamerization and characterization of the Arabidopsis AAA ATPase CDC48A complex using forster resonance energy transfer-fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy and fluorescence correlation spectroscopy
Abstract
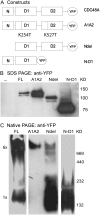
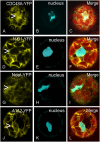
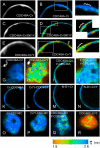
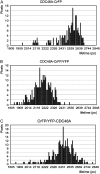
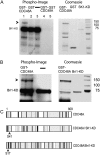
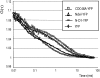
The Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) AAA ATPase CDC48A was fused to cerulean fluorescent protein and yellow fluorescent protein. AAA ATPases like CDC48 are only active in hexameric form. Förster resonance energy transfer-based fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy using CDC48A-cerulean fluorescent protein and CDC48A-yellow fluorescent protein showed interaction between two adjacent protomers, demonstrating homo-oligomerization occurs in living plant cells. Interaction between CDC48A and the SOMATIC EMBRYOGENESIS RECEPTOR-LIKE KINASE1 (SERK1) transmembrane receptor occurs in very restricted domains at the plasma membrane. In these domains the predominant form of the fluorescently tagged CDC48A protein is a hexamer, suggesting that SERK1 is associated with the active form of CDC48A in vivo. SERK1 trans-phosphorylates CDC48A on Ser-41. Förster resonance energy transfer-fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy was used to show that in vivo the C-terminal domains of CDC48A stay in close proximity. Employing fluorescence correlation spectroscopy, it was shown that CDC48A hexamers are part of larger complexes.
Figures
References
-
- Aker J, Borst JW, Karlova R, de Vries S (2006) The Arabidopsis thaliana AAA protein CDC48A interacts in vivo with the somatic embryogenesis receptor-like kinase 1 receptor at the plasma membrane. J Struct Biol 156 62–71 - PubMed
-
- Borst JW, Hink M, van Hoek A, Visser AJWG (2005) Effects of refractive index and viscosity on fluorescence and anisotropy decays of enhanced cyan and yellow fluorescent proteins. J Fluoresc 15 153–160 - PubMed
-
- Clayton AH, Walker F, Orchard SG, Henderson DF, Rothacker J, Nice EC, Burgess AW (2005) Ligand-induced dimer-tetramer transition during the activation of the cell surface epidermal growth factor receptor-A multidimensional microscopy analysis. J Biol Chem 280 30392–30399 - PubMed
-
- Davies JM, Tsuruta H, May AP, Weis WI (2005) Conformational changes of p97 during nucleotide hydrolysis determined by small-angle X-Ray scattering. Structure 13 183–195 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

