Loss of integrin alpha(v)beta8 on dendritic cells causes autoimmunity and colitis in mice
- PMID: 17694047
- PMCID: PMC2670239
- DOI: 10.1038/nature06110
Loss of integrin alpha(v)beta8 on dendritic cells causes autoimmunity and colitis in mice
Abstract
The cytokine transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) is an important negative regulator of adaptive immunity. TGF-beta is secreted by cells as an inactive precursor that must be activated to exert biological effects, but the mechanisms that regulate TGF-beta activation and function in the immune system are poorly understood. Here we show that conditional loss of the TGF-beta-activating integrin alpha(v)beta8 on leukocytes causes severe inflammatory bowel disease and age-related autoimmunity in mice. This autoimmune phenotype is largely due to lack of alpha(v)beta8 on dendritic cells, as mice lacking alpha(v)beta8 principally on dendritic cells develop identical immunological abnormalities as mice lacking alpha(v)beta8 on all leukocytes, whereas mice lacking alpha(v)beta8 on T cells alone are phenotypically normal. We further show that dendritic cells lacking alpha(v)beta8 fail to induce regulatory T cells (T(R) cells) in vitro, an effect that depends on TGF-beta activity. Furthermore, mice lacking alpha(v)beta8 on dendritic cells have reduced proportions of T(R) cells in colonic tissue. These results suggest that alpha(v)beta8-mediated TGF-beta activation by dendritic cells is essential for preventing immune dysfunction that results in inflammatory bowel disease and autoimmunity, effects that are due, at least in part, to the ability of alpha(v)beta8 on dendritic cells to induce and/or maintain tissue T(R) cells.
Figures
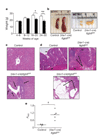
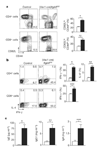
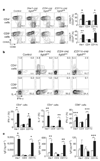

Comment in
-
Dendritic cells, TGF-beta, and Integrin alphavbeta8 in inflammatory bowel disease: a tolerogenic "ménage à trois".Gastroenterology. 2008 Jan;134(1):354-5. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2007.11.050. Gastroenterology. 2008. PMID: 18166365 No abstract available.
References
-
- Marie JC, Liggitt D, Rudensky AY. Cellular mechanisms of fatal early-onset autoimmunity in mice with the T cell-specific targeting of transforming growth factor-β receptor. Immunity. 2006;25:441–454. - PubMed
-
- Li MO, Sanjabi S, Flavell RA. Transforming growth factor-β controls development, homeostasis, and tolerance of T cells by regulatory T cell-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Immunity. 2006;25:455–471. - PubMed
-
- Annes JP, Munger JS, Rifkin DB. Making sense of latent TGFβ activation. J. Cell Sci. 2003;116:217–224. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

