A distal single nucleotide polymorphism alters long-range regulation of the PU.1 gene in acute myeloid leukemia
- PMID: 17694175
- PMCID: PMC1937499
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI30525
A distal single nucleotide polymorphism alters long-range regulation of the PU.1 gene in acute myeloid leukemia
Abstract
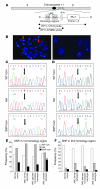
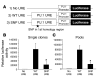
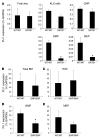
Targeted disruption of a highly conserved distal enhancer reduces expression of the PU.1 transcription factor by 80% and leads to acute myeloid leukemia (AML) with frequent cytogenetic aberrations in mice. Here we identify a SNP within this element in humans that is more frequent in AML with a complex karyotype, leads to decreased enhancer activity, and reduces PU.1 expression in myeloid progenitors in a development-dependent manner. This SNP inhibits binding of the chromatin-remodeling transcriptional regulator special AT-rich sequence binding protein 1 (SATB1). Overexpression of SATB1 increased PU.1 expression, and siRNA inhibition of SATB1 downregulated PU.1 expression. Targeted disruption of the distal enhancer led to a loss of regulation of PU.1 by SATB1. Interestingly, disruption of SATB1 in mice led to a selective decrease of PU.1 RNA in specific progenitor types (granulocyte-macrophage and megakaryocyte-erythrocyte progenitors) and a similar effect was observed in AML samples harboring this SNP. Thus we have identified a SNP within a distal enhancer that is associated with a subtype of leukemia and exerts a deleterious effect through remote transcriptional dysregulation in specific progenitor subtypes.
Figures


References
-
- Scott E.W., Simon M.C., Anastasi J., Singh H. Requirement of transcription factor PU.1 in the development of multiple hematopoietic lineages. Science. 1994;265:1573–1577. - PubMed
-
- Tenen D.G., Hromas R., Licht J.D., Zhang D.E. Transcription factors, normal myeloid development, and leukemia. Blood. 1997;90:489–519. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

