Automatic brachytherapy seed placement under MRI guidance
- PMID: 17694871
- PMCID: PMC3099459
- DOI: 10.1109/TBME.2007.900816
Automatic brachytherapy seed placement under MRI guidance
Abstract
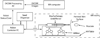
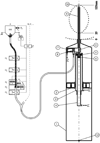
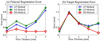
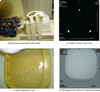
The paper presents a robotic method of performing low dose rate prostate brachytherapy under magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) guidance. The design and operation of a fully automated MR compatible seed injector is presented. This is used with the MrBot robot for transperineal percutaneous prostate access. A new image-registration marker and algorithms are also presented. The system is integrated and tested with a 3T MRI scanner. Tests compare three different registration methods, assess the precision of performing automated seed deployment, and use the seeds to assess the accuracy of needle targeting under image guidance. Under the ideal conditions of the in vitro experiments, results show outstanding image-guided needle and seed placement accuracy.
Figures


References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Murray T, Xu J, Smigal C, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics, 2006. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2006;vol. 56:106–130. - PubMed
-
- Naitoh J, Zeiner RL, Dekernion JB. Diagnosis and treatment of prostate cancer. Am. Family Physician. 1998;vol. 57:1531. –+, - PubMed
-
- Ash D, Bottomley DM, Carey BM. Prostate brachytherapy. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 1998;vol. 1:185–188. - PubMed
-
- Langley SEM, Laing R. Prostate brachytherapy has come of age: A review of the technique and results. BJU Int. 2002;vol. 89:241–249. - PubMed
-
- Vicini FA, Kini VR, Edmundson G, Gustafson GS, Stromberg J, Martinez A. A comprehensive review of prostate cancer brachytherapy: Defining an optimal technique. Int. J. Radiation Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1999;vol. 44:483–491. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

