Human wild-type alanine:glyoxylate aminotransferase and its naturally occurring G82E variant: functional properties and physiological implications
- PMID: 17696873
- PMCID: PMC2049084
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20070637
Human wild-type alanine:glyoxylate aminotransferase and its naturally occurring G82E variant: functional properties and physiological implications
Abstract
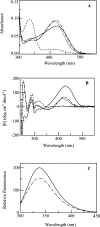
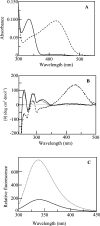
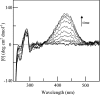
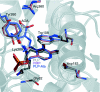
Human hepatic peroxisomal AGT (alanine:glyoxylate aminotransferase) is a PLP (pyridoxal 5'-phosphate)-dependent enzyme whose deficiency causes primary hyperoxaluria Type I, a rare autosomal recessive disorder. To acquire experimental evidence for the physiological function of AGT, the K(eq),(overall) of the reaction, the steady-state kinetic parameters of the forward and reverse reactions, and the pre-steady-state kinetics of the half-reactions of the PLP form of AGT with L-alanine or glycine and the PMP (pyridoxamine 5'-phosphate) form with pyruvate or glyoxylate have been measured. The results indicate that the enzyme is highly specific for catalysing glyoxylate to glycine processing, thereby playing a key role in glyoxylate detoxification. Analysis of the reaction course also reveals that PMP remains bound to the enzyme during the catalytic cycle and that the AGT-PMP complex displays a reactivity towards oxo acids higher than that of apoAGT in the presence of PMP. These findings are tentatively related to possible subtle rearrangements at the active site also indicated by the putative binding mode of catalytic intermediates. Additionally, the catalytic and spectroscopic features of the naturally occurring G82E variant have been analysed. Although, like the wild-type, the G82E variant is able to bind 2 mol PLP/dimer, it exhibits a significant reduced affinity for PLP and even more for PMP compared with wild-type, and an altered conformational state of the bound PLP. The striking molecular defect of the mutant, consisting in the dramatic decrease of the overall catalytic activity (approximately 0.1% of that of normal AGT), appears to be related to the inability to undergo an efficient transaldimination of the PLP form of the enzyme with amino acids as well as an efficient conversion of AGT-PMP into AGT-PLP. Overall, careful biochemical analyses have allowed elucidation of the mechanism of action of AGT and the way in which the disease causing G82E mutation affects it.
Figures




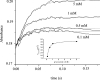
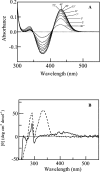

Similar articles
-
Molecular Insight into the Synergism between the Minor Allele of Human Liver Peroxisomal Alanine:Glyoxylate Aminotransferase and the F152I Mutation.J Biol Chem. 2009 Mar 27;284(13):8349-58. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M808965200. Epub 2009 Jan 20. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19155213 Free PMC article.
-
Human liver peroxisomal alanine:glyoxylate aminotransferase: Different stability under chemical stress of the major allele, the minor allele, and its pathogenic G170R variant.Biochimie. 2010 Dec;92(12):1801-11. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2010.08.005. Epub 2010 Aug 14. Biochimie. 2010. PMID: 20713123
-
Overexpression of human alanine:glyoxylate aminotransferase in Escherichia coli: renaturation from guanidine-HCl and affinity for pyridoxal phosphate co-factor.Protein Expr Purif. 2005 May;41(1):18-26. doi: 10.1016/j.pep.2004.11.004. Protein Expr Purif. 2005. PMID: 15802217
-
Human liver peroxisomal alanine:glyoxylate aminotransferase: characterization of the two allelic forms and their pathogenic variants.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011 Nov;1814(11):1577-84. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2010.12.005. Epub 2010 Dec 20. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011. PMID: 21176891 Review.
-
Protein homeostasis defects of alanine-glyoxylate aminotransferase: new therapeutic strategies in primary hyperoxaluria type I.Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:687658. doi: 10.1155/2013/687658. Epub 2013 Jul 16. Biomed Res Int. 2013. PMID: 23956997 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Insight into the Synergism between the Minor Allele of Human Liver Peroxisomal Alanine:Glyoxylate Aminotransferase and the F152I Mutation.J Biol Chem. 2009 Mar 27;284(13):8349-58. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M808965200. Epub 2009 Jan 20. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19155213 Free PMC article.
-
A synthesis and quantification method for endogenous metabolites dimethylguanidino valeric acid.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 1;15(1):11100. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-94932-z. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40169761 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure of the S187F variant of human liver alanine: glyoxylate [corrected] aminotransferase associated with primary hyperoxaluria type I and its functional implications.Proteins. 2013 Aug;81(8):1457-65. doi: 10.1002/prot.24300. Epub 2013 Jun 1. Proteins. 2013. PMID: 23589421 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of hepatic oxalate overproduction ameliorates metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis.Nat Metab. 2024 Oct;6(10):1939-1962. doi: 10.1038/s42255-024-01134-4. Epub 2024 Sep 27. Nat Metab. 2024. PMID: 39333384 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical Studies on Human Ornithine Aminotransferase Support a Cell-Based Enzyme Replacement Therapy in the Gyrate Atrophy of the Choroid and Retina.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 19;25(14):7931. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147931. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39063173 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Danpure C. J., Fryer P., Griffiths S., Guttridge K. M., Jennings P. R., Allsop J., Moser A. B., Naidu S., Moser H. W., MacCollin M., et al. Cytosolic compartmentalization of hepatic alanine:glyoxylate aminotransferase in patients with aberrant peroxisomal biogenesis and its effect on oxalate metabolism. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 1994;17:27–40. - PubMed
-
- Lumb M. J., Danpure C. J. Functional synergism between the most common polymorphism in human alanine:glyoxylate aminotransferase and four of the most common disease-causing mutations. J. Biol. Chem. 2000;275:36415–36422. - PubMed
-
- Purdue P. E., Lumb M. J., Allsop J., Minatogawa Y., Danpure C. J. A glycine-to-glutamate substitution abolishes alanine:glyoxylate aminotransferase catalytic activity in a subset of patients with primary hyperoxaluria type 1. Genomics. 1992;13:215–218. - PubMed
-
- Zhang X., Roe S. M., Hou Y., Bartlam M., Rao Z., Pearl L. H., Danpure C. J. Crystal structure of alanine:glyoxylate aminotransferase and the relationship between genotype and enzymatic phenotype in primary hyperoxaluria type 1. J. Mol. Biol. 2003;331:643–652. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

