Detection of knockdown resistance (kdr) mutations in Anopheles gambiae: a comparison of two new high-throughput assays with existing methods
- PMID: 17697325
- PMCID: PMC1971715
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2875-6-111
Detection of knockdown resistance (kdr) mutations in Anopheles gambiae: a comparison of two new high-throughput assays with existing methods
Abstract
Background: Knockdown resistance (kdr) is a well-characterized mechanism of resistance to pyrethroid insecticides in many insect species and is caused by point mutations of the pyrethroid target site the para-type sodium channel. The presence of kdr mutations in Anopheles gambiae, the most important malaria vector in Africa, has been monitored using a variety of molecular techniques. However, there are few reports comparing the performance of these different assays. In this study, two new high-throughput assays were developed and compared with four established techniques.
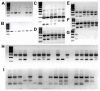
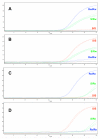
Methods: Fluorescence-based assays based on 1) TaqMan probes and 2) high resolution melt (HRM) analysis were developed to detect kdr alleles in An. gambiae. Four previously reported techniques for kdr detection, Allele Specific Polymerase Chain Reaction (AS-PCR), Heated Oligonucleotide Ligation Assay (HOLA), Sequence Specific Oligonucleotide Probe - Enzyme-Linked ImmunoSorbent Assay (SSOP-ELISA) and PCR-Dot Blot were also optimized. The sensitivity and specificity of all six assays was then compared in a blind genotyping trial of 96 single insect samples that included a variety of kdr genotypes and African Anopheline species. The relative merits of each assay was assessed based on the performance in the genotyping trial, the length/difficulty of each protocol, cost (both capital outlay and consumable cost), and safety (requirement for hazardous chemicals).
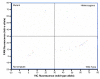
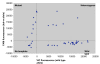
Results: The real-time TaqMan assay was both the most sensitive (with the lowest number of failed reactions) and the most specific (with the lowest number of incorrect scores). Adapting the TaqMan assay to use a PCR machine and endpoint measurement with a fluorimeter showed a slight reduction in sensitivity and specificity. HRM initially gave promising results but was more sensitive to both DNA quality and quantity and consequently showed a higher rate of failure and incorrect scores. The sensitivity and specificity of AS-PCR, SSOP-ELISA, PCR Dot Blot and HOLA was fairly similar with a small number of failures and incorrect scores.
Conclusion: The results of blind genotyping trials of each assay indicate that where maximum sensitivity and specificity are required the TaqMan real-time assay is the preferred method. However, the cost of this assay, particularly in terms of initial capital outlay, is higher than that of some of the other methods. TaqMan assays using a PCR machine and fluorimeter are nearly as sensitive as real-time assays and provide a cost saving in capital expenditure. If price is a primary factor in assay choice then the AS-PCR, SSOP-ELISA, and HOLA are all reasonable alternatives with the SSOP-ELISA approach having the highest throughput.
Figures

References
-
- Phillips-Howard PA, Nahlen BL, Kolczak MS, Hightower AW, ter Kuile FO, Alaii JA, Gimnig JE, Arudo J, Vulule JM, Odhacha A, Kachur SP, Schoute E, Rosen DH, Sexton JD, Oloo AJ, Hawley WA. Efficacy of permethrin-treated bed nets in the prevention of mortality in young children in an area of high perennial malaria transmission in western Kenya. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2003;68:23–29. - PubMed
-
- Binka FN, Kubaje A, Adjuik M, Williams LA, Lengeler C, Maude GH, Armah GE, Kajihara B, Adiamah JH, Smith PG. Impact of permethrin impregnated bednets on child mortality in Kassena-Nankana district, Ghana: A randomized controlled trial. Trop Med Int Health. 1996;1:147–154. - PubMed
-
- Choi HW, Breman JG, Teutsch SM, Liu SM, Hightower AW, Sexton JD. The effectiveness of insecticide-impregnated bed nets in reducing cases of malaria infection: A meta-analysis of published results. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1995;52:377–382. - PubMed
-
- D'Alessandro U, Olaleye BO, McGuire W, Langerock P, Bennett S, Aikins MK, Thomson MC, Cham MK, Cham BA, Greenwood BM. Mortality and morbidity from malaria in Gambian children after introduction of an impregnated bednet program. Lancet. 1995;345:479–483. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(95)90582-0. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Vulule JM, Beach RF, Atieli FK, Roberts JM, Mount DL, Mwangi RW. Reduced susceptibility of Anopheles gambiae to permethrin associated with the use of permethrin-impregnated bednets and curtains in Kenya. Med Vet Entomol. 1994;8:71–75. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

