Influence of dextran-70 on systemic inflammatory response and myocardial ischaemia-reperfusion following cardiac operations
- PMID: 17697359
- PMCID: PMC2206488
- DOI: 10.1186/cc6095
Influence of dextran-70 on systemic inflammatory response and myocardial ischaemia-reperfusion following cardiac operations
Abstract
Introduction: Experimental studies have demonstrated that dextran-70 reduces the leukocyte-endothelium interaction, but clinical evidence is still lacking. Our objective was to justify the anti-inflammatory effect of dextran-70 following cardiac operations.
Methods: Forty patients undergoing coronary bypass surgery (n = 32) or aortic valve replacement (n = 8) were enrolled in this prospective, randomized, double-blind study. Two groups were formed. In group A (n = 20), dextran-70 infusion was administered at a dose of 7.5 ml/kg before the initiation of cardiopulmonary bypass and at a dose of 12.5 ml/kg after the cessation of cardiopulmonary bypass. Group B served as a control with identical amounts of gelatin infusion (n = 20). The plasma concentration of procalcitonin, C-reactive protein, IL 6, IL 6r, IL 8, IL 10, soluble endothelial leukocyte adhesion molecule-1, soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1, cardiac troponin-I and various haemodynamic parameters were measured in the perioperative period. Multivariate methods were used for statistical analysis.
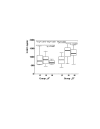
Results: In group A, lower peak (median) plasma levels of procalcitonin (0.2 versus 1.4, p < 0.001), IL 8 (5.6 versus 94.8, p < 0.001), IL 10 (47.2 versus 209.7, p = 0.001), endothelial leukocyte adhesion molecule-1 (88.5 versus 130.6, p = 0.033), intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (806.7 versus 1,375.7, P = 0.001) and troponin-I (0.22 versus 0.66, p = 0.018) were found. There was no significant difference in IL 6, IL-6r and C-reactive protein values between groups. Higher figures of the cardiac index (p = 0.010) along with reduced systemic vascular resistance (p = 0.005) were noted in group A.
Conclusion: Our investigation demonstrated that the use of dextran-70 reduces the systemic inflammatory response and cardiac troponin-I release following cardiac operation.
Trial registration number: ISRCTN38289094.
Figures


Comment in
-
Dextran-70 to modulate inflammatory response after cardiopulmonary bypass: potential for a novel approach?Crit Care. 2007;11(5):163. doi: 10.1186/cc6103. Crit Care. 2007. PMID: 17850682 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Asimakopoulos G. Systemic inflammation and cardiac surgery: an update. Perfusion. 2001;16:353–360. - PubMed
-
- Sablotzki A, Friedrich I, Mühling J, Dehne MG, Spillner J, Silber RE, Czeslik E. The systemic inflammatory response syndrome following cardiac surgery: different expression of proinflammatory cytokines and procalcitonin in patients with and without multiorgan dysfunctions. Perfusion. 2002;17:103–109. doi: 10.1191/0267659102pf543oa. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kerbaul F, Guidon C, Lejeune PJ, Mollo M, Mesana T, Gouin F. Hyperprocalcitonemia is related to noninfectious postoperative severe systemic inflammatory response syndrome associated with cardiovascular dysfunction after coronary artery bypass graft surgery. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2002;16:47–53. doi: 10.1053/jcan.2002.29672. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

