Trends in resistance to penicillin and erythromycin of invasive pneumococci in Portugal
- PMID: 17697443
- PMCID: PMC2870878
- DOI: 10.1017/S0950268807009405
Trends in resistance to penicillin and erythromycin of invasive pneumococci in Portugal
Abstract
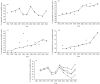
Antimicrobial resistance of pneumococci is influenced by serotypes, antimicrobial consumption and vaccine use. Serotyping of 697 out of 1331 pneumococcal isolates, recovered in Portugal from 1994 to 2004, showed that the theoretical rate of heptavalent conjugate vaccine coverage was 91.7% and 63.6% for penicillin and erythromycin non-susceptible strains, respectively, in children up to 1 year old. The use of amoxicillin and erythromycin decreased in the vaccine period 2001-2004 (P=0.04 and P<0.01, respectively) but azithromycin usage increased in the same period (P<0.01). By using linear regression models, we evaluated the role of antimicrobial and vaccine use in the trends of resistance to penicillin and erythromycin among the isolates. The models suggest that the use of macrolides was the main factor associated with an increase of penicillin and erythromycin non-susceptible isolates from adults (P<0.01) and erythromycin non-susceptible isolates among children (P=0.006). These models also suggest that heptavalent vaccine is failing to reduce antimicrobial resistance as expected, possibly due to the increased consumption of azithromycin (P=0.04). The efficient use of new antibiotics may reverse the present trends of antimicrobial resistance.
Figures


References
-
- Klugman KP. The successful clone: the vector of dissemination of resistance in Streptococcus pneumoniae. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy. 2002;50:1–5. - PubMed
-
- Klein JO. The epidemiology of pneumococcal disease in infants and children. Reviews of Infectious Diseases. 1981;3:246–253. - PubMed
-
- Felmingham D et al. Surveillance of resistance in bacteria causing community-acquired respiratory tract infections. Clinical Microbiology and Infection. 2002;8:12–42. (Suppl. 2): - PubMed
-
- Goossens H et al. Outpatient antibiotic use in Europe and association with resistance: a cross-national database study. Lancet. 2005;365:579–587. - PubMed
-
- Bruinsma N et al. Trends of penicillin and erythromycin resistance among invasive Streptococcus pneumoniae in Europe. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy. 2004;54:1045–1050. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

