The O antigen enables Bordetella parapertussis to avoid Bordetella pertussis-induced immunity
- PMID: 17698566
- PMCID: PMC2044517
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00763-07
The O antigen enables Bordetella parapertussis to avoid Bordetella pertussis-induced immunity
Abstract
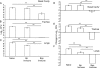
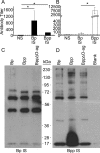
Bordetella pertussis and Bordetella parapertussis are closely related endemic human pathogens which cause whooping cough, a disease that is reemerging in human populations. Despite how closely related these pathogens are, their coexistence and the limited efficacy of B. pertussis vaccines against B. parapertussis suggest a lack of cross-protective immunity between the two. We sought to address the ability of infection-induced immunity against one of these pathogens to protect against subsequent infection by the other using a mouse model of infection. Immunity induced by B. parapertussis infection protected against subsequent infections by either species. However, immunity induced by B. pertussis infection prevented subsequent B. pertussis infections but did not protect against B. parapertussis infections. The O antigen of B. parapertussis inhibited binding of antibodies to the bacterial surface and was required for B. parapertussis to colonize mice convalescent from B. pertussis infection. Thus, the O antigen of B. parapertussis confers asymmetrical cross-immunity between the causative agents of whooping cough. We propose that these findings warrant investigation of the relative role of B. parapertussis in the resurgence of whooping cough.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A recombinant iron transport protein from Bordetella pertussis confers protection against Bordetella parapertussis.Microbiol Immunol. 2017 Oct;61(10):407-415. doi: 10.1111/1348-0421.12532. Epub 2017 Sep 26. Microbiol Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28857261
-
Bordetella parapertussis survives the innate interaction with human neutrophils by impairing bactericidal trafficking inside the cell through a lipid raft-dependent mechanism mediated by the lipopolysaccharide O antigen.Infect Immun. 2012 Dec;80(12):4309-16. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00662-12. Epub 2012 Oct 1. Infect Immun. 2012. PMID: 23027528 Free PMC article.
-
O antigen allows B. parapertussis to evade B. pertussis vaccine-induced immunity by blocking binding and functions of cross-reactive antibodies.PLoS One. 2009 Sep 14;4(9):e6989. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0006989. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19750010 Free PMC article.
-
Bordetella pertussis, B. parapertussis, vaccines and cycles of whooping cough.Pathog Dis. 2015 Oct;73(7):ftv055. doi: 10.1093/femspd/ftv055. Epub 2015 Aug 4. Pathog Dis. 2015. PMID: 26242280 Review.
-
Surveillance of pertussis: methods and implementation.Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2016 Jul;14(7):657-67. doi: 10.1080/14787210.2016.1190272. Epub 2016 May 31. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2016. PMID: 27224518 Review.
Cited by
-
Evidence for horizontal gene transfer of two antigenically distinct O antigens in Bordetella bronchiseptica.Infect Immun. 2009 Aug;77(8):3249-57. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01448-08. Epub 2009 Jun 15. Infect Immun. 2009. PMID: 19528223 Free PMC article.
-
Highlights of the 14th International Bordetella Symposium.mSphere. 2025 Jun 25;10(6):e0018925. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00189-25. Epub 2025 May 16. mSphere. 2025. PMID: 40377335 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Darwin review: the evolution of virulence in human pathogens.Proc Biol Sci. 2024 Feb 14;291(2016):20232043. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2023.2043. Epub 2024 Feb 7. Proc Biol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38320607 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prior exposure to Bordetella species as an exclusion criterion in the baboon model of pertussis.J Vet Med Sci. 2017 Jan 20;79(1):60-64. doi: 10.1292/jvms.16-0427. Epub 2016 Sep 26. J Vet Med Sci. 2017. PMID: 27666464 Free PMC article.
-
Immunomodulation as a Novel Strategy for Prevention and Treatment of Bordetella spp. Infections.Front Immunol. 2019 Dec 13;10:2869. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02869. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31921136 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anderson, R. M. 1995. Evolutionary pressures in the spread and persistence of infectious agents in vertebrate populations. Parasitology 111(Suppl.):S15-S31. - PubMed
-
- Arico, B., R. Gross, J. Smida, and R. Rappuoli. 1987. Evolutionary relationships in the genus Bordetella. Mol. Microbiol. 1:301-308. - PubMed
-
- Bergfors, E., B. Trollfors, J. Taranger, T. Lagergard, V. Sundh, and G. Zackrisson. 1999. Parapertussis and pertussis: differences and similarities in incidence, clinical course, and antibody responses. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 3:140-146. - PubMed
-
- Bjornstad, O. N., and E. T. Harvill. 2005. Evolution and emergence of Bordetella in humans. Trends Microbiol. 13:355-359. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

