Requirement for T-bet in the aberrant differentiation of unhelped memory CD8+ T cells
- PMID: 17698591
- PMCID: PMC2118697
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20070841
Requirement for T-bet in the aberrant differentiation of unhelped memory CD8+ T cells
Abstract
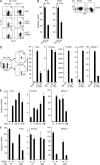
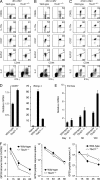
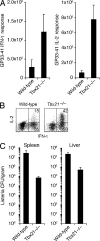
Immunity to intracellular pathogens requires dynamic balance between terminal differentiation of short-lived, cytotoxic effector CD8+ T cells and self-renewal of central-memory CD8+ T cells. We now show that T-bet represses transcription of IL-7Ralpha and drives differentiation of effector and effector-memory CD8+ T cells at the expense of central-memory cells. We also found T-bet to be overexpressed in CD8+ T cells that differentiated in the absence of CD4+ T cell help, a condition that is associated with defective central-memory formation. Finally, deletion of T-bet corrected the abnormal phenotypic and functional properties of "unhelped" memory CD8+ T cells. T-bet, thus, appears to function as a molecular switch between central- and effector-memory cell differentiation. Antagonism of T-bet may, therefore, represent a novel strategy to offset dysfunctional programming of memory CD8+ T cells.
Figures
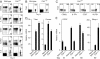
References
-
- Williams, M.A., and M.J. Bevan. 2007. Effector and memory CTL differentiation. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 25:171–192. - PubMed
-
- Sallusto, F., D. Lenig, R. Forster, M. Lipp, and A. Lanzavecchia. 1999. Two subsets of memory T lymphocytes with distinct homing potentials and effector functions. Nature. 401:708–712. - PubMed
-
- Wherry, E.J., V. Teichgraber, T.C. Becker, D. Masopust, S.M. Kaech, R. Antia, U.H. von Andrian, and R. Ahmed. 2003. Lineage relationship and protective immunity of memory CD8 T cell subsets. Nat. Immunol. 4:225–234. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

