Duplicate VegfA genes and orthologues of the KDR receptor tyrosine kinase family mediate vascular development in the zebrafish
- PMID: 17698971
- PMCID: PMC2077312
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2006-04-016378
Duplicate VegfA genes and orthologues of the KDR receptor tyrosine kinase family mediate vascular development in the zebrafish
Abstract
Vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA) and the type III receptor tyrosine kinase receptors (RTKs) are both required for the differentiation of endothelial cells (vasculogenesis) and for the sprouting of new capillaries (angiogenesis). We have isolated a duplicated zebrafish VegfA locus, termed VegfAb, and a duplicate RTK locus with homology to KDR/FLK1 (named Kdrb). Morpholino-disrupted VegfAb embryos develop a normal circulatory system until approximately 2 to 3 days after fertilization (dpf), when defects in angiogenesis permit blood to extravasate into many tissues. Unlike the VegfAa(121) and VegfAa(165) isoforms, the VegfAb isoforms VegfAb(171) and VegfAb(210) are not normally secreted when expressed in mammalian tissue culture cells. The Kdrb locus encodes a 1361-amino acid transmembrane receptor with strong homology to mammalian KDR. Combined knockdown of both RTKs leads to defects in vascular development, suggesting that they cooperate in mediating the vascular effects of VegfA in zebrafish development. Both VegfAa and VegfAb can individually bind and promote phosphorylation of both Flk1 (Kdra) and Kdrb proteins in vitro. Taken together, our data support a model in the zebrafish, in which duplicated VegfA and multiple type III RTKs mediate vascular development.
Figures



 ). At 2 dpf, vegfAa121 is expressed in the developing heart vasculature and pectoral fins. The aortic vasculature is also identified in vegfAb in situs, but in contrast, only vegfAb is expressed in the developing pronephros (◀). At 4 dpf, significant expression is restricted to vegfAb in the vasculature surrounding the eye. (B) Wild-type embryos were analyzed by whole-mount in situ hybridization with a probe to either kdrb (top panels) or kdra (bottom panels) at 16 somites (left panels), 2 dpf (middle panels), and 4 dpf (right panels). At 16 somites, expression is limited to the inner cell mass. By 2 dpf, the developing intersomitic vasculature expresses both kdrb and kdra. At 4 dpf, both genes are expressed in the developing subintestinal veins (SIVs) and in the remaining vasculature. See “In situ hybridization and photography” for image acquisition information.
). At 2 dpf, vegfAa121 is expressed in the developing heart vasculature and pectoral fins. The aortic vasculature is also identified in vegfAb in situs, but in contrast, only vegfAb is expressed in the developing pronephros (◀). At 4 dpf, significant expression is restricted to vegfAb in the vasculature surrounding the eye. (B) Wild-type embryos were analyzed by whole-mount in situ hybridization with a probe to either kdrb (top panels) or kdra (bottom panels) at 16 somites (left panels), 2 dpf (middle panels), and 4 dpf (right panels). At 16 somites, expression is limited to the inner cell mass. By 2 dpf, the developing intersomitic vasculature expresses both kdrb and kdra. At 4 dpf, both genes are expressed in the developing subintestinal veins (SIVs) and in the remaining vasculature. See “In situ hybridization and photography” for image acquisition information.
 , ◀ in panels D and F) and aberrant head vascular development. SIVs were severely reduced in number, size, and branching that was more pronounced anteriorly. (E) At 4 dpf, blood is apparent in the head and anterior embryos (
, ◀ in panels D and F) and aberrant head vascular development. SIVs were severely reduced in number, size, and branching that was more pronounced anteriorly. (E) At 4 dpf, blood is apparent in the head and anterior embryos ( ), which (F) corresponds to the areas with defects in angiogenesis. (G) Control morpholino–injected embryos demonstrate normal subintestinal vein (SIV) architecture by alkaline phosphatase staining, and (H) RBCs are shown by staining with o-dianisidine that stains hemoglobin reddish/brown. However, (I) injection of either morpholino targeting VegfAb leads to SIVs that are erratically placed and thin or nearly completely absent (only the start codon morpholino is shown) and (J) extravasation of RBCs in various structures, which is more pronounced anteriorly where the angiogenic defects are most visible (B-F). The results are combined from at least 3 separate experiments, and the photomicrographs are representative of the visible defects.
), which (F) corresponds to the areas with defects in angiogenesis. (G) Control morpholino–injected embryos demonstrate normal subintestinal vein (SIV) architecture by alkaline phosphatase staining, and (H) RBCs are shown by staining with o-dianisidine that stains hemoglobin reddish/brown. However, (I) injection of either morpholino targeting VegfAb leads to SIVs that are erratically placed and thin or nearly completely absent (only the start codon morpholino is shown) and (J) extravasation of RBCs in various structures, which is more pronounced anteriorly where the angiogenic defects are most visible (B-F). The results are combined from at least 3 separate experiments, and the photomicrographs are representative of the visible defects.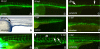
 ) in 34 (33%) of 101 injected embryos. Embryos coinjected with morpholinos targeting both kdra/b had severe axial vessel defects, although some subintestinal vasculature is apparent. The results are combined from at least 4 separate experiments and the photomicrographs are representative of the visible defects.
) in 34 (33%) of 101 injected embryos. Embryos coinjected with morpholinos targeting both kdra/b had severe axial vessel defects, although some subintestinal vasculature is apparent. The results are combined from at least 4 separate experiments and the photomicrographs are representative of the visible defects.
References
-
- Klagsbrun M, Takashima S, Mamluk R. The role of neuropilin in vascular and tumor biology. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2002;515:33–48. - PubMed
-
- Risau W. Mechanisms of angiogenesis. Nature. 1997;386:671–674. - PubMed
-
- Ferrara N, Carver-Moore K, Chen H, et al. Heterozygous embryonic lethality induced by targeted inactivation of the VEGF gene. Nature. 1996;380:439–442. - PubMed
-
- Carmeliet P, Ferreira V, Breier G, et al. Abnormal blood vessel development and lethality in embryos lacking a single VEGF allele. Nature. 1996;380:435–439. - PubMed
-
- Carmeliet P, Moons L, Dewerchin M, et al. Insights in vessel development and vascular disorders using targeted inactivation and transfer of vascular endothelial growth factor, the tissue factor receptor, and the plasminogen system. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1997;811:191–206. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

