Viral sequence evolution in acute hepatitis C virus infection
- PMID: 17699568
- PMCID: PMC2168804
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00995-07
Viral sequence evolution in acute hepatitis C virus infection
Abstract
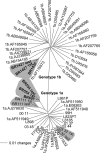
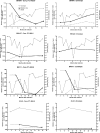
CD8(+)-T-cell responses play an important role in the containment and clearance of hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection, and an association between viral persistence and development of viral escape mutations has been postulated. While escape from CD8+ -T-cell responses has been identified as a major driving force for the evolution of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV), a broader characterization of this relationship is needed in HCV infection. To determine the extent, kinetics, and driving forces of HCV sequence evolution, we sequenced the entire HCV genome longitudinally in four subjects monitored for up to 30 months after acute infection. For two subjects the transmission sources were also available. Of 53 total non-envelope amino acid substitutions detected, a majority represented forward mutations away from the consensus sequence. In contrast to studies in HIV and SIV, however, only 11% of these were associated with detectable CD8+ T-cell responses. Interestingly, 19% of non-envelope mutations represented changes toward the consensus sequence, suggesting reversion in the absence of immune pressure upon transmission. Notably, the rate of evolution of forward and reverse mutations correlated with the conservation of each residue, which is indicative of structural constraints influencing the kinetics of viral evolution. Finally, the rate of sequence evolution was observed to decline over the course of infection, possibly reflective of diminishing selection pressure by dysfunctional CD8+ T cells. Taken together, these data provide insight into the extent to which HCV is capable of evading early CD8+ T-cell responses and support the hypothesis that dysfunction of CD8+ T cells may be associated with failure to resolve HCV infections.
Figures


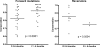
References
-
- Allen, T. M., M. Altfeld, S. C. Geer, E. T. Kalife, C. Moore, M. O'Sullivan, K., I. Desouza, M. E. Feeney, R. L. Eldridge, E. L. Maier, D. E. Kaufmann, M. P. Lahaie, L. Reyor, G. Tanzi, M. N. Johnston, C. Brander, R. Draenert, J. K. Rockstroh, H. Jessen, E. S. Rosenberg, S. A. Mallal, and B. D. Walker. 2005. Selective escape from CD8+ T-cell responses represents a major driving force of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) sequence diversity and reveals constraints on HIV-1 evolution. J. Virol. 79:13239-13249. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Allen, T. M., M. Altfeld, X. G. Yu, K. M. O'Sullivan, M. Lichterfeld, S. Le Gall, M. John, B. R. Mothe, P. K. Lee, E. T. Kalife, D. E. Cohen, K. A. Freedberg, D. A. Strick, M. N. Johnston, A. Sette, E. S. Rosenberg, S. A. Mallal, P. J. Goulder, C. Brander, and B. D. Walker. 2004. Selection, transmission, and reversion of an antigen-processing cytotoxic T-lymphocyte escape mutation in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. J. Virol. 78:7069-7078. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Allen, T. M., D. H. O'Connor, P. Jing, J. L. Dzuris, B. R. Mothe, T. U. Vogel, E. Dunphy, M. E. Liebl, C. Emerson, N. Wilson, K. J. Kunstman, X. Wang, D. B. Allison, A. L. Hughes, R. C. Desrosiers, J. D. Altman, S. M. Wolinsky, A. Sette, and D. I. Watkins. 2000. Tat-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes select for SIV escape variants during resolution of primary viraemia. Nature 407:386-390. - PubMed
-
- Bain, C., A. Fatmi, F. Zoulim, J. P. Zarski, C. Trepo, and G. Inchauspe. 2001. Impaired allostimulatory function of dendritic cells in chronic hepatitis C infection. Gastroenterology 120:512-524. - PubMed
-
- Barouch, D. H., J. Kunstman, M. J. Kuroda, J. E. Schmitz, S. Santra, F. W. Peyerl, G. R. Krivulka, K. Beaudry, M. A. Lifton, D. A. Gorgone, D. C. Montefiori, M. G. Lewis, S. M. Wolinsky, and N. L. Letvin. 2002. Eventual AIDS vaccine failure in a rhesus monkey by viral escape from cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Nature 415:335-339. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

