The topology of hepatitis B virus pregenomic RNA promotes its replication
- PMID: 17699570
- PMCID: PMC2168771
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01414-07
The topology of hepatitis B virus pregenomic RNA promotes its replication
Abstract
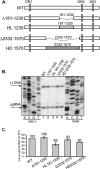
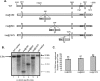
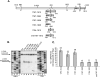
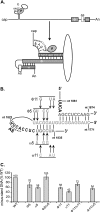
Previous analysis of hepatitis B virus (HBV) indicated base pairing between two cis-acting sequences, the 5' half of the upper stem of epsilon and phi, contributes to the synthesis of minus-strand DNA. Our goal was to identify other cis-acting sequences on the pregenomic RNA (pgRNA) involved in the synthesis of minus-strand DNA. We found that large portions of the pgRNA could be deleted or substituted without an appreciable decrease in the level of minus-strand DNA synthesized, indicating that most of the pgRNA is dispensable and that a specific size of the pgRNA is not required for this process. Our results indicated that the cis-acting sequences for the synthesis of minus-strand DNA are present near the 5' and 3' ends of the pgRNA. In addition, we found that the first-strand template switch could be directed to a new location when a 72-nucleotide (nt) fragment, which contained the cis-acting sequences present near the 3' end of the pgRNA, was introduced at that location. Within this 72-nt region, we uncovered two new cis-acting sequences, which flank the acceptor site. We show that one of these sequences, named omega and located 3' of the acceptor site, base pairs with phi to contribute to the synthesis of minus-strand DNA. Thus, base pairing between three cis-acting elements (5' half of the upper stem of epsilon, phi, and omega) are necessary for the synthesis of HBV minus-strand DNA. We propose that this topology of pgRNA facilitates first-strand template switch and/or the initiation of synthesis of minus-strand DNA.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Base pairing between the 5' half of epsilon and a cis-acting sequence, phi, makes a contribution to the synthesis of minus-strand DNA for human hepatitis B virus.J Virol. 2006 May;80(9):4380-7. doi: 10.1128/JVI.80.9.4380-4387.2006. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16611897 Free PMC article.
-
A novel cis-acting element facilitates minus-strand DNA synthesis during reverse transcription of the hepatitis B virus genome.J Virol. 2004 Jun;78(12):6252-62. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.12.6252-6262.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15163718 Free PMC article.
-
cis-Acting sequences that contribute to synthesis of minus-strand DNA are not conserved between hepadnaviruses.J Virol. 2010 Dec;84(24):12824-31. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01487-10. Epub 2010 Oct 6. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20926578 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis B virus reverse transcriptase and its many roles in hepadnaviral genomic replication.Infect Agents Dis. 1994 Apr-Jun;3(2-3):85-93. Infect Agents Dis. 1994. PMID: 7529120 Review.
-
Hepatitis B virus replication.World J Gastroenterol. 2007 Jan 7;13(1):48-64. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i1.48. World J Gastroenterol. 2007. PMID: 17206754 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Core protein: A pleiotropic keystone in the HBV lifecycle.Antiviral Res. 2015 Sep;121:82-93. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2015.06.020. Epub 2015 Jun 27. Antiviral Res. 2015. PMID: 26129969 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Controllable inhibition of hepatitis B virus replication by a DR1-targeting short hairpin RNA (shRNA) expressed from a DOX-inducible lentiviral vector.Virus Genes. 2013 Jun;46(3):393-403. doi: 10.1007/s11262-013-0886-2. Epub 2013 Feb 9. Virus Genes. 2013. PMID: 23397077 Free PMC article.
-
Reverse transcriptase- and RNA packaging signal-dependent incorporation of APOBEC3G into hepatitis B virus nucleocapsids.J Virol. 2008 Jul;82(14):6852-61. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00465-08. Epub 2008 May 14. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18480459 Free PMC article.
-
The interface between hepatitis B virus capsid proteins affects self-assembly, pregenomic RNA packaging, and reverse transcription.J Virol. 2015 Mar;89(6):3275-84. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03545-14. Epub 2015 Jan 7. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25568211 Free PMC article.
-
Ultra-deep pyrosequencing analysis of the hepatitis B virus preCore region and main catalytic motif of the viral polymerase in the same viral genome.Nucleic Acids Res. 2011 Oct;39(19):8457-71. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr451. Epub 2011 Jul 8. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011. PMID: 21742757 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Geballe, A. P., R. R. Spaete, and E. S. Mocarski. 1986. A cis-acting element within the 5′ leader of a cytomegalovirus β transcript determines kinetic class. Cell 46:865-872. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

