Transcriptional modulation of genes encoding structural characteristics of differentiating enterocytes during development of a polarized epithelium in vitro
- PMID: 17699590
- PMCID: PMC2043570
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e07-04-0308
Transcriptional modulation of genes encoding structural characteristics of differentiating enterocytes during development of a polarized epithelium in vitro
Abstract
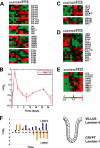
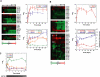
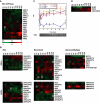
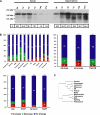
Although there is considerable evidence implicating posttranslational mechanisms in the development of epithelial cell polarity, little is known about the patterns of gene expression and transcriptional regulation during this process. We characterized the temporal program of gene expression during cell-cell adhesion-initiated polarization of human Caco-2 cells in tissue culture, which develop structural and functional polarity similar to that of enterocytes in vivo. A distinctive switch in gene expression patterns occurred upon formation of cell-cell contacts between neighboring cells. Expression of genes involved in cell proliferation was down-regulated concomitant with induction of genes necessary for functional specialization of polarized epithelial cells. Transcriptional up-regulation of these latter genes correlated with formation of important structural and functional features in enterocyte differentiation and establishment of structural and functional cell polarity; components of the apical microvilli were induced as the brush border formed during polarization; as barrier function was established, expression of tight junction transmembrane proteins peaked; transcripts encoding components of the apical, but not the basal-lateral trafficking machinery were increased during polarization. Coordinated expression of genes encoding components of functional cell structures were often observed indicating temporal control of expression and assembly of multiprotein complexes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Parallels between global transcriptional programs of polarizing Caco-2 intestinal epithelial cells in vitro and gene expression programs in normal colon and colon cancer.Mol Biol Cell. 2007 Nov;18(11):4245-60. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e07-04-0309. Epub 2007 Aug 15. Mol Biol Cell. 2007. PMID: 17699589 Free PMC article.
-
The dual role of annexin II in targeting of brush border proteins and in intestinal cell polarity.Differentiation. 2011 Apr;81(4):243-52. doi: 10.1016/j.diff.2011.01.009. Epub 2011 Feb 16. Differentiation. 2011. PMID: 21330046
-
A cryptic sequence targets the adhesion complex scaffold ANKS4B to apical microvilli to promote enterocyte brush border assembly.J Biol Chem. 2020 Sep 4;295(36):12588-12604. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.013790. Epub 2020 Jul 6. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32636301 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the Crumbs proteins in ciliogenesis, cell migration and actin organization.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2018 Sep;81:13-20. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2017.10.018. Epub 2017 Oct 24. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2018. PMID: 29056580 Review.
-
Transcriptional Control of Apical-Basal Polarity Regulators.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 15;22(22):12340. doi: 10.3390/ijms222212340. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34830224 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Actin polymerization and depolymerization in developing vertebrates.Front Physiol. 2023 Sep 8;14:1213668. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1213668. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37745245 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Coordinated protein sorting, targeting and distribution in polarized cells.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008 Nov;9(11):833-45. doi: 10.1038/nrm2525. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18946473 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TCF4 and CDX2, major transcription factors for intestinal function, converge on the same cis-regulatory regions.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Aug 24;107(34):15157-62. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1003822107. Epub 2010 Aug 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20696899 Free PMC article.
-
Incomplete coverage of candidate genes: a poorly considered bias.Curr Genomics. 2007 Nov;8(7):476-83. doi: 10.2174/138920207783591681. Curr Genomics. 2007. PMID: 19412419 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium levels in the Golgi complex regulate clustering and apical sorting of GPI-APs in polarized epithelial cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Aug 17;118(33):e2014709118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2014709118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 34389665 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aijaz S., Balda M. S., Matter K. Tight junctions: molecular architecture and function. Int. Rev. Cytol. 2006;248:261–298. - PubMed
-
- Aspenstrom P. The verprolin family of proteins: regulators of cell morphogenesis and endocytosis. FEBS Lett. 2005;579:5253–5259. - PubMed
-
- Athman R., Louvard D., Robine S. The epithelial cell cytoskeleton and intracellular trafficking. III. How is villin involved in the actin cytoskeleton dynamics in intestinal cells? Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2002;283:G496–G502. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

