FGF-2 release from the lens capsule by MMP-2 maintains lens epithelial cell viability
- PMID: 17699594
- PMCID: PMC2043559
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e06-05-0416
FGF-2 release from the lens capsule by MMP-2 maintains lens epithelial cell viability
Abstract
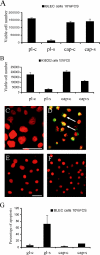
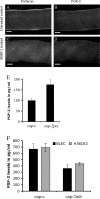
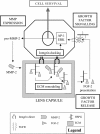
The lens is an avascular tissue, separated from the aqueous and vitreous humors by its own extracellular matrix, the lens capsule. Here we demonstrate that the lens capsule is a source of essential survival factors for lens epithelial cells. Primary and immortalized lens epithelial cells survive in low levels of serum and are resistant to staurosporine-induced apoptosis when they remain in contact with the lens capsule. Physical contact with the capsule is required for maximal resistance to stress. The lens capsule is also a source of soluble factors including fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF-2) and perlecan, an extracellular matrix component that enhances FGF-2 activity. Matrix metalloproteinase 2 (MMP-2) inhibition as well as MMP-2 pretreatment of lens capsules greatly reduced the protective effect of the lens capsule, although this could be largely reversed by the addition of either conditioned medium or recombinant FGF-2. These data suggest that FGF-2 release from the lens capsule by MMP-2 is essential to lens epithelial cell viability and survival.
Figures
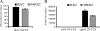

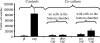


Similar articles
-
A gradient of matrix-bound FGF-2 and perlecan is available to lens epithelial cells.Exp Eye Res. 2014 Mar;120(100):10-4. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2013.12.004. Epub 2013 Dec 14. Exp Eye Res. 2014. PMID: 24341990 Free PMC article.
-
MMP inhibition prevents human lens epithelial cell migration and contraction of the lens capsule.Br J Ophthalmol. 2004 Jul;88(7):868-72. doi: 10.1136/bjo.2003.034629. Br J Ophthalmol. 2004. PMID: 15205227 Free PMC article.
-
FGF: an autocrine regulator of human lens cell growth independent of added stimuli.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2001 May;42(6):1305-11. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2001. PMID: 11328744
-
Generation of transparency and cellular organization in lens explants.Exp Eye Res. 2008 May;86(5):734-45. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2008.01.020. Epub 2008 Feb 3. Exp Eye Res. 2008. PMID: 18343368
-
FGF-2 counteracts loss of TGFbeta affected cells from rat lens explants: implications for PCO (after cataract).Mol Vis. 2004 Jul 22;10:521-32. Mol Vis. 2004. PMID: 15303087
Cited by
-
Metalloprotease inhibitor TIMP proteins control FGF-2 bioavailability and regulate skeletal growth.J Cell Biol. 2019 Sep 2;218(9):3134-3152. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201906059. Epub 2019 Aug 1. J Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 31371388 Free PMC article.
-
Prevention of posterior capsule opacification through intracapsular hydrogen peroxide or distilled water treatment in human donor tissue.Sci Rep. 2018 Aug 24;8(1):12739. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-31178-y. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30143742 Free PMC article.
-
An Atlas of Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycans in the Postnatal Rat Lens.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2021 Nov 1;62(14):5. doi: 10.1167/iovs.62.14.5. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2021. PMID: 34730792 Free PMC article.
-
Characterizing molecular diffusion in the lens capsule.Matrix Biol. 2010 Apr;29(3):228-36. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2009.12.004. Epub 2009 Dec 22. Matrix Biol. 2010. PMID: 20026402 Free PMC article.
-
Patterns of gene expression in microarrays and expressed sequence tags from normal and cataractous lenses.Hum Genomics. 2012 Sep 1;6(1):14. doi: 10.1186/1479-7364-6-14. Hum Genomics. 2012. PMID: 23244575 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams J. C., Watt F. M. Regulation of development and differentiation by the extracellular matrix. Development. 1993;117:1183–1198. - PubMed
-
- Andley U. P., Rhim J. S., Chylack L. T., Jr, Fleming T. P. Propagation and immortalization of human lens epithelial cells in culture. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1994;35:3094–3102. - PubMed
-
- Azuma N., Hara T. Extracellular matrix of opacified anterior capsule after endocapsular cataract surgery. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 1998;236:531–536. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

