Rab6 regulates both ZW10/RINT-1 and conserved oligomeric Golgi complex-dependent Golgi trafficking and homeostasis
- PMID: 17699596
- PMCID: PMC1995728
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e07-01-0080
Rab6 regulates both ZW10/RINT-1 and conserved oligomeric Golgi complex-dependent Golgi trafficking and homeostasis
Abstract
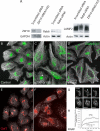
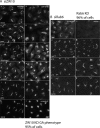
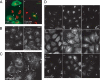
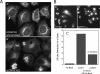
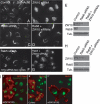
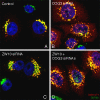
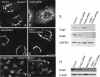
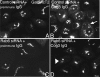
We used multiple approaches to investigate the role of Rab6 relative to Zeste White 10 (ZW10), a mitotic checkpoint protein implicated in Golgi/endoplasmic reticulum (ER) trafficking/transport, and conserved oligomeric Golgi (COG) complex, a putative tether in retrograde, intra-Golgi trafficking. ZW10 depletion resulted in a central, disconnected cluster of Golgi elements and inhibition of ERGIC53 and Golgi enzyme recycling to ER. Small interfering RNA (siRNA) against RINT-1, a protein linker between ZW10 and the ER soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptor, syntaxin 18, produced similar Golgi disruption. COG3 depletion fragmented the Golgi and produced vesicles; vesicle formation was unaffected by codepletion of ZW10 along with COG, suggesting ZW10 and COG act separately. Rab6 depletion did not significantly affect Golgi ribbon organization. Epistatic depletion of Rab6 inhibited the Golgi-disruptive effects of ZW10/RINT-1 siRNA or COG inactivation by siRNA or antibodies. Dominant-negative expression of guanosine diphosphate-Rab6 suppressed ZW10 knockdown induced-Golgi disruption. No cross-talk was observed between Rab6 and endosomal Rab5, and Rab6 depletion failed to suppress p115 (anterograde tether) knockdown-induced Golgi disruption. Dominant-negative expression of a C-terminal fragment of Bicaudal D, a linker between Rab6 and dynactin/dynein, suppressed ZW10, but not COG, knockdown-induced Golgi disruption. We conclude that Rab6 regulates distinct Golgi trafficking pathways involving two separate protein complexes: ZW10/RINT-1 and COG.
Figures


References
-
- Allan B. B., Moyer B. D., Balch W. E. Rab1 recruitment of p115 into a cis-SNARE complex: programming budding COPII vesicles for fusion. Science. 2000;289:444–448. - PubMed
-
- Andag U., Schmitt H. H. Dsl1p, an essential component of the Golgi-endoplasmic reticulum retrieval system in yeast, uses the same sequence motif to interact with different subunits of the COPI vesicle coat. J. Biol. Chem. 2003;278:51722–51734. - PubMed
-
- Antony C., Cibert C., Geraud G., Santa Maria A., Maro B., Mayau V., Goud B. The small GTP-binding protein rab6p is distributed from medial Golgi to the traan-Golgi network as determined by a confocal microscopic approach. J. Cell Sci. 1992;103:785–796. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

