Functions of OsBZR1 and 14-3-3 proteins in brassinosteroid signaling in rice
- PMID: 17699623
- PMCID: PMC1959469
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0706386104
Functions of OsBZR1 and 14-3-3 proteins in brassinosteroid signaling in rice
Abstract
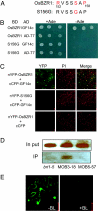
Brassinosteroids (BR) are essential growth hormones found throughout the plant kingdom. BR bind to the receptor kinase BRI1 on the cell surface to activate a signal transduction pathway that regulates nuclear gene expression and plant growth. To understand the downstream BR signaling mechanism in rice, we studied the function of OsBZR1 using reverse genetic approaches and identified OsBZR1-interacting proteins. Suppressing OsBZR1 expression by RNAi resulted in dwarfism, erect leaves, reduced BR sensitivity, and altered BR-responsive gene expression in transgenic rice plants, demonstrating an essential role of OsBZR1 in BR responses in rice. Moreover, a yeast two-hybrid screen identified 14-3-3 proteins as OsBZR1-interacting proteins. Mutation of a putative 14-3-3-binding site of OsBZR1 abolished its interaction with the 14-3-3 proteins in yeast and in vivo. Such mutant OsBZR1 proteins suppressed the phenotypes of the Arabidopsis bri1-5 mutant and showed an increased nuclear distribution compared with the wild-type protein, suggesting that 14-3-3 proteins directly inhibit OsBZR1 function at least in part by reducing its nuclear localization. These results demonstrate a conserved function of OsBZR1 and an important role of 14-3-3 proteins in brassinosteroid signal transduction in rice.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Vert G, Nemhauser JL, Geldner N, Hong F, Chory J. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2005;21:177–201. - PubMed
-
- Clouse SD, Sasse JM. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol. 1998;49:427–451. - PubMed
-
- Bishop GJ. J Plant Growth Regul. 2003;22:325–335. - PubMed
-
- Sakamoto T, Morinaka Y, Ohnishi T, Sunohara H, Fujioka S, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Mizutani M, Sakata K, Takatsuto S, Yoshida S, et al. Nat Biotechnol. 2006;24:105–109. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

