Role of purine-rich exonic splicing enhancers in nuclear retention of pre-mRNAs
- PMID: 17699631
- PMCID: PMC1959442
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0704922104
Role of purine-rich exonic splicing enhancers in nuclear retention of pre-mRNAs
Abstract
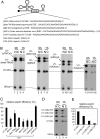
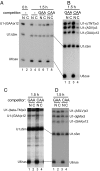
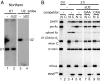
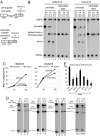
Intron-containing pre-mRNAs are normally retained in the nucleus until they are spliced to produce mature mRNAs that are exported to the cytoplasm. Although the detailed mechanism is not well understood, the formation of splicing-related complexes on pre-mRNAs is thought to be responsible for the nuclear retention. Therefore, pre-mRNAs containing suboptimal splice sites should tend to leak out to the cytoplasm. Such pre-mRNAs often contain purine-rich exonic splicing enhancers (ESEs) that stimulate splicing of the adjacent intron. Here, we show that ESEs per se possess an activity to retain RNAs in the nucleus through a saturable nuclear retention factor. Cross-competition experiments revealed that intron-containing pre-mRNAs (without ESEs) used the same saturable nuclear retention factor as ESEs. Interestingly, although intronless mRNAs containing ESEs were also poorly exported, spliced mRNAs produced from ESE-containing pre-mRNAs were efficiently exported to the cytoplasm. Thus, the splicing reaction can reset the nuclear retention state caused by ESEs, allowing nuclear export of mature mRNAs. Our results reveal a novel aspect of ESE activity that should contribute to gene expression and RNA quality control.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Factors associated with a purine-rich exonic splicing enhancer sequence in Xenopus oocyte nucleus.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007 Aug 3;359(3):580-5. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.05.144. Epub 2007 May 30. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007. PMID: 17548051
-
Exonic splicing enhancers contribute to the use of both 3' and 5' splice site usage of rat beta-tropomyosin pre-mRNA.RNA. 1999 Mar;5(3):378-94. doi: 10.1017/s1355838299981050. RNA. 1999. PMID: 10094307 Free PMC article.
-
Complex expression pattern of RPGR reveals a role for purine-rich exonic splicing enhancers.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2002 Nov;43(11):3373-82. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2002. PMID: 12407146
-
Initial splice-site recognition and pairing during pre-mRNA splicing.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1996 Apr;6(2):215-20. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(96)80053-0. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1996. PMID: 8722179 Review.
-
Exonic splicing enhancers: mechanism of action, diversity and role in human genetic diseases.Trends Biochem Sci. 2000 Mar;25(3):106-10. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(00)01549-8. Trends Biochem Sci. 2000. PMID: 10694877 Review.
Cited by
-
Frame-disrupting mutations elicit pre-mRNA accumulation independently of frame disruption.Nucleic Acids Res. 2010 Mar;38(5):1559-74. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp1115. Epub 2009 Dec 9. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010. PMID: 20007599 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of a constitutively active calcineurin encoded by an intron-retaining mRNA in follicular keratinocytes.PLoS One. 2011 Mar 14;6(3):e17685. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017685. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21423799 Free PMC article.
-
Detained introns are a novel, widespread class of post-transcriptionally spliced introns.Genes Dev. 2015 Jan 1;29(1):63-80. doi: 10.1101/gad.247361.114. Genes Dev. 2015. PMID: 25561496 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of HPV-16 L1 expression from L1 cDNAs correlates with the presence of hnRNP A1 binding sites in the L1 coding region.Virus Genes. 2008 Feb;36(1):45-53. doi: 10.1007/s11262-007-0174-0. Epub 2007 Nov 27. Virus Genes. 2008. PMID: 18040766
-
ORC1 binds to cis-transcribed RNAs for efficient activation of replication origins.Nat Commun. 2023 Jul 24;14(1):4447. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-40105-3. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37488096 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tran EJ, Wente SR. Cell. 2006;125:1041–1053. - PubMed
-
- Vinciguerra P, Stutz F. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2004;16:285–292. - PubMed
-
- DeCerbo J, Carmichael GG. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2005;17:302–308. - PubMed
-
- Wolin SL, Cedervall T. Annu Rev Biochem. 2002;71:375–403. - PubMed
-
- Henras AK, Dez C, Henry Y. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2004;14:335–343. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

