Capsule gene analysis of invasive Haemophilus influenzae: accuracy of serotyping and prevalence of IS1016 among nontypeable isolates
- PMID: 17699642
- PMCID: PMC2045354
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.00794-07
Capsule gene analysis of invasive Haemophilus influenzae: accuracy of serotyping and prevalence of IS1016 among nontypeable isolates
Abstract
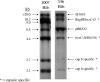
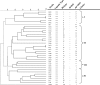
We evaluated the accuracy of serologic capsule typing by analyzing capsule genes and related markers among invasive Haemophilus influenzae isolates before and after the introduction of H. influenzae serotype b (Hib) conjugate vaccines. Three hundred and sixty invasive H. influenzae isolates were collected as part of Active Bacterial Core surveillance within the Georgia Emerging Infections Program between 1 January 1989 and 31 July 1998. All isolates were biotyped, serotyped by slide agglutination serotyping (SAST), and evaluated using PCR capsule typing. Nontypeable H. influenzae (NTHi) isolates were probed with Hib cap-gene-containing plasmid pUO38 and with IS1016; a subset was examined with phosphoglucose isomerase (pgi) genotyping and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE). Discrepancies between SAST and PCR capsule typing were found for 64/360 (17.5%) of the isolates; 48 encapsulated by SAST were NTHi by PCR, 8 NTHi by SAST were encapsulated by PCR, 6 encapsulated by SAST were a different capsule type by PCR, and 2 encapsulated by SAST were capsule-deficient Hib variants (Hib-minus). None of the PCR-confirmed NTHi isolates demonstrated homology with residual capsule gene sequences; 19/201 (9.5%) had evidence of IS1016, an insertion element associated with division I H. influenzae capsule serotypes. The majority of IS1016-positive NTHi were biotypes I and V and showed some genetic relatedness by PFGE. In conclusion, PCR capsule typing was more accurate than SAST and Hib-minus variants were rare. IS1016 was present in 9.5% of NTHi isolates, suggesting that this subset may be more closely related to encapsulated organisms. A better understanding of NTHi may contribute to vaccine development.
Figures


Comment in
-
Serotyping and population genetics of invasive Haemophilus influenzae.J Clin Microbiol. 2008 Mar;46(3):1159. doi: 10.1128/JCM.02166-07. J Clin Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18326837 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Adderson, E. E., C. L. Byington, L. Spencer, A. Kimball, M. Hindiyeh, K. Carroll, S. Mottice, E. K. Korgenski, J. C. Christenson, and A. T. Pavia. 2001. Invasive serotype a Haemophilus influenzae infections with a virulence genotype resembling Haemophilus influenzae type b: emerging pathogen in the vaccine era? Pediatrics 108:E18. - PubMed
-
- Bolivar, F., R. L. Rodriguez, P. J. Greene, M. C. Betlach, H. L. Heyneker, and H. W. Boyer. 1977. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene 2:95-113. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

