Validation of nasopharyngeal sampling and culture techniques for detection of Streptococcus pneumoniae in children in Kenya
- PMID: 17699645
- PMCID: PMC2045369
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.01393-07
Validation of nasopharyngeal sampling and culture techniques for detection of Streptococcus pneumoniae in children in Kenya
Abstract
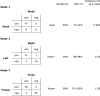
We compared nasopharyngeal swabs against nasal wash cultures for detecting colonizing pneumococci and examined the effect of frozen storage in skim milk-tryptone-glucose-glycerin on culture. Among the 55 children with positive nasal wash cultures, swab cultures were positive for 47 (85%). Of the 96 swabs positive on direct plating, 94 (98%) were positive when recultured after freezing.
Figures
References
-
- Gibson, L. F., and J. T. Khoury. 1986. Storage and survival of bacteria by ultra-freeze. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 3:127-129.
-
- Hendley, J. O., M. A. Sande, P. M. Stewart, and J. M. Gwaltney, Jr. 1975. Spread of Streptococcus pneumoniae in Families. I. Carriage rates and distribution of types. J. Infect. Dis. 132:55-61. - PubMed
-
- O'Brien, K., H. Nohynek, et al. 2003. The pneumococcal vaccine trials carriage working group. Report from a WHO working group: standard method for detecting upper respiratory carriage of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 22:133-140. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

