Social stress enhances sympathetic innervation of primate lymph nodes: mechanisms and implications for viral pathogenesis
- PMID: 17699667
- PMCID: PMC6672171
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1247-07.2007
Social stress enhances sympathetic innervation of primate lymph nodes: mechanisms and implications for viral pathogenesis
Abstract
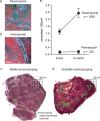
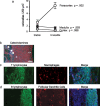
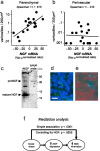
Behavioral processes regulate immune system function in part via direct sympathetic innervation of lymphoid organs, but little is known about the factors that regulate the architecture of neural fibers in lymphoid tissues. In the present study, we find that experimentally imposed social stress can enhance the density of catecholaminergic neural fibers within axillary lymph nodes from adult rhesus macaques. This effect is linked to increased transcription of the key sympathetic neurotrophin nerve growth factor and occurs predominately in extrafollicular regions of the paracortex that contain T-lymphocytes and macrophages. Functional consequences of stress-induced increases in innervation density include reduced type I interferon response to viral infection and increased replication of the simian immunodeficiency virus. These data reveal a surprising degree of behaviorally induced plasticity in the structure of lymphoid innervation and define a novel pathway by which social factors can modulate immune response and viral pathogenesis.
Figures

References
-
- Agy MB, Acker RL, Sherbert CH, Katze MG. Interferon treatment inhibits virus replication in HIV-1- and SIV-infected CD4+ T-cell lines by distinct mechanisms: evidence for decreased stability and aberrant processing of HIV-1 proteins. Virology. 1995;214:379–386. - PubMed
-
- Angeletti PU, Levi-Montalcini R, Caramia F. Analysis of the effects of the antiserum to the nerve growth factor in adult mice. Brain Res. 1971;27:343–355. - PubMed
-
- Bellinger DL, Lorton D, Lubahn C, Felten DL. Innervation of lymphoid organs—association of nerves with cells of the immune system and their implications in disease. In: Ader R, Felten DL, Cohen N, editors. Psychoneuroimmunology. Ed 3. San Diego: Academic; 2001. pp. 55–111.
-
- Canto-Nogues C, Jones S, Sangster R, Silvera P, Hull R, Cook R, Hall G, Walker B, Stott EJ, Hockley D, Almond N. In situ hybridization and immunolabelling study of the early replication of simian immunodeficiency virus (SIVmacJ5) in vivo. J Gen Virol. 2001;82:2225–2234. - PubMed
-
- Capitanio JP, Lerche NW. Social separation, housing relocation, and survival in simian AIDS: a retrospective analysis. Psychosom Med. 1998;60:235–244. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
