Feedback regulation of p38 activity via ATF2 is essential for survival of embryonic liver cells
- PMID: 17699753
- PMCID: PMC1948861
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.430207
Feedback regulation of p38 activity via ATF2 is essential for survival of embryonic liver cells
Abstract
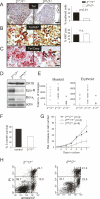
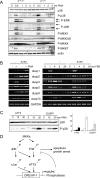
The ATF2 transcription factor is phosphorylated by the stress-activated mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) JNK and p38. We show that this phosphorylation is essential for ATF2 function in vivo, since a mouse carrying mutations in the critical phosphorylation sites has a strong phenotype identical to that seen upon deletion of the DNA-binding domain. In addition, combining this mutant with a knockout of the ATF2 homolog, ATF7, results in embryonic lethality with severe abnormalities in the developing liver and heart. The mutant fetal liver is characterized by high levels of apoptosis in developing hepatocytes and haematopoietic cells. Furthermore, we observe a significant increase in active p38 due to loss of a negative feedback loop involving the ATF2-dependent transcriptional activation of MAPK phosphatases. In embryonic liver cells, this increase drives apoptosis, since it can be suppressed by chemical inhibition of p38. Our findings demonstrate the importance of finely regulating the activities of MAPKs during development.
Figures





References
-
- Adams R.H., Porras A., Alonso G., Jones M., Vintersten K., Panelli S., Valladares A., Perez L., Klein R., Nebreda A.R., Porras A., Alonso G., Jones M., Vintersten K., Panelli S., Valladares A., Perez L., Klein R., Nebreda A.R., Alonso G., Jones M., Vintersten K., Panelli S., Valladares A., Perez L., Klein R., Nebreda A.R., Jones M., Vintersten K., Panelli S., Valladares A., Perez L., Klein R., Nebreda A.R., Vintersten K., Panelli S., Valladares A., Perez L., Klein R., Nebreda A.R., Panelli S., Valladares A., Perez L., Klein R., Nebreda A.R., Valladares A., Perez L., Klein R., Nebreda A.R., Perez L., Klein R., Nebreda A.R., Klein R., Nebreda A.R., Nebreda A.R. Essential role of p38α MAP kinase in placental but not embryonic cardiovascular development. Mol. Cell. 2000;6:109–116. - PubMed
-
- Beg A.A., Sha W.C., Bronson R.T., Ghosh S., Baltimore D., Sha W.C., Bronson R.T., Ghosh S., Baltimore D., Bronson R.T., Ghosh S., Baltimore D., Ghosh S., Baltimore D., Baltimore D. Embryonic lethality and liver degeneration in mice lacking the RelA component of NF-κ B. Nature. 1995;376:167–170. - PubMed
-
- Behrens A., Sibilia M., Wagner E.F., Sibilia M., Wagner E.F., Wagner E.F. Amino-terminal phosphorylation of c-Jun regulates stress-induced apoptosis and cellular proliferation. Nat. Genet. 1999;21:326–329. - PubMed
-
- Behrens A., Sabapathy K., Graef I., Cleary M., Crabtree G.R., Wagner E.F., Sabapathy K., Graef I., Cleary M., Crabtree G.R., Wagner E.F., Graef I., Cleary M., Crabtree G.R., Wagner E.F., Cleary M., Crabtree G.R., Wagner E.F., Crabtree G.R., Wagner E.F., Wagner E.F. Jun N-terminal kinase 2 modulates thymocyte apoptosis and T cell activation through c-Jun and nuclear factor of activated T cell (NF-AT) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2001;98:1769–1774. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Benbrook D.M., Jones N.C., Jones N.C. Heterodimer formation between CREB and JUN proteins. Oncogene. 1990;5:295–302. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
