Taurine release in developing mouse hippocampus is modulated by glutathione and glutathione derivatives
- PMID: 17701096
- PMCID: PMC2814815
- DOI: 10.1007/s00726-007-0587-z
Taurine release in developing mouse hippocampus is modulated by glutathione and glutathione derivatives
Abstract
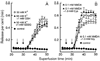
Glutathione (reduced form GSH and oxidized form GSSG) constitutes an important defense against oxidative stress in the brain, and taurine is an inhibitory neuromodulator particularly in the developing brain. The effects of GSH and GSSG and glycylglycine, gamma-glutamylcysteine, cysteinylglycine, glycine and cysteine on the release of [(3)H]taurine evoked by K+-depolarization or the ionotropic glutamate receptor agonists glutamate, kainate, 2-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionate (AMPA) and N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) were now studied in slices from the hippocampi from 7-day-old mouse pups in a perfusion system. All stimulatory agents (50 mM K(+), 1 mM glutamate, 0.1 mM kainate, 0.1 mM AMPA and 0.1 mM NMDA) evoked taurine release in a receptor-mediated manner. Both GSH and GSSG significantly inhibited the release evoked by 50 mM K+. The release induced by AMPA and glutamate was also inhibited, while the kainate-evoked release was significantly activated by both GSH and GSSG. The NMDA-evoked release proved the most sensitive to modulation: L-Cysteine and glycine enhanced the release in a concentration-dependent manner, whereas GSH and GSSG were inhibitory at low (0.1 mM) but not at higher (1 or 10 mM) concentrations. The release evoked by 0.1 mM AMPA was inhibited by gamma-glutamylcysteine and cysteinylglycine, whereas glycylglycine had no effect. The 0.1 mM NMDA-evoked release was inhibited by glycylglycine and gamma-glutamylcysteine. In turn, cysteinylglycine inhibited the NMDA-evoked release at 0.1 mM, but was inactive at 1 mM. Glutathione exhibited both enhancing and attenuating effects on taurine release, depending on the glutathione concentration and on the agonist used. Both glutathione and taurine act as endogenous neuroprotective effectors during early postnatal life.
Figures
References
-
- Bergles DE, Roberts JDB, Somogyi P, Jahr CE. Glutamatergic synapses on oligodendrocyte precursor cells in the hippocampus. Nature. 2000;405:187–191. - PubMed
-
- Condorelli DF, Conti F, Gallo V, Kirchhoff F, Seifert G, Steinhäuser C, Verkhratsky A, Yuan X. Expression and functional analysis of glutamate receptors in glial cells. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1999;468:49–67. - PubMed
-
- Devreker F, Van den Bergh M, Biramane J, Winston RML, Englert Y, Hardy K. Effects of taurine on human embryo development in vitro. Human Reprod. 1999;14:2350–2356. - PubMed
-
- Dunah AW, Yasuda RP, Wang Y, Luo J, Dávila-Garcia MI, Gbadegesin M, Vicini S, Wolfe BB. Regional and ontogenic expression of the NMDA receptor subunit NR2D protein in rat brain using a subunit-specific antibody. J Neurochem. 1996;67:2335–2345. - PubMed
-
- El Idrissi A, Trenkner E. Taurine regulates mitochondrial calcium homeostasis. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2003;526:527–536. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

