Lethal contractural syndrome type 3 (LCCS3) is caused by a mutation in PIP5K1C, which encodes PIPKI gamma of the phophatidylinsitol pathway
- PMID: 17701898
- PMCID: PMC1950840
- DOI: 10.1086/520771
Lethal contractural syndrome type 3 (LCCS3) is caused by a mutation in PIP5K1C, which encodes PIPKI gamma of the phophatidylinsitol pathway
Abstract
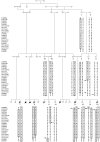
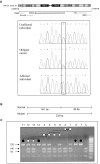
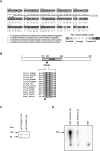
Lethal congenital contractural syndrome (LCCS) is a severe form of arthrogryposis. To date, two autosomal recessive forms of the disease (LCCS and LCCS2) have been described and mapped to chromosomes 9q34 and 12q13, respectively. We now describe a third LCCS phenotype (LCCS3)--similar to LCCS2 yet without neurogenic bladder. Using 10K single-nucleotide-polymorphism arrays, we mapped the disease-associated gene to 8.8 Mb on chromosome 19p13. Further analysis using microsatallite markers narrowed the locus to a 3.4-Mb region harboring 120 genes. Of these genes, 30 candidates were sequenced, which identified a single homozygous mutation in PIP5K1C. PIP5K1C encodes phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate 5-kinase, type I, gamma (PIPKI gamma ), an enzyme that phophorylates phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate to generate phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate (PIP(2)). We demonstrate that the mutation causes substitution of aspartic acid with asparagine at amino acid 253 (D253N), abrogating the kinase activity of PIPKI gamma . Thus, a defect in the phosphatidylinositol pathway leading to a decrease in synthesis of PIP(2), a molecule active in endocytosis of synaptic vesicle proteins, culminates in lethal congenital arthrogryposis.
Figures
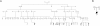

Similar articles
-
Lethal congenital contractural syndrome type 2 (LCCS2) is caused by a mutation in ERBB3 (Her3), a modulator of the phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase/Akt pathway.Am J Hum Genet. 2007 Sep;81(3):589-95. doi: 10.1086/520770. Epub 2007 Jul 24. Am J Hum Genet. 2007. PMID: 17701904 Free PMC article.
-
Autosomal recessive lethal congenital contractural syndrome type 4 (LCCS4) caused by a mutation in MYBPC1.Hum Mutat. 2012 Oct;33(10):1435-8. doi: 10.1002/humu.22122. Epub 2012 Jun 7. Hum Mutat. 2012. PMID: 22610851
-
Homozygosity mapping of lethal congenital contractural syndrome type 2 (LCCS2) to a 6 cM interval on chromosome 12q13.Am J Med Genet A. 2004 Oct 15;130A(3):272-6. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.30266. Am J Med Genet A. 2004. PMID: 15378541
-
Phosphatidylinositol phosphate kinases.J Endocrinol Invest. 2004;27(6 Suppl):137-42. J Endocrinol Invest. 2004. PMID: 15481814 Review.
-
Friedreich's ataxia and frataxin: molecular genetics, evolution and pathogenesis (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2001 Jun;7(6):581-9. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.7.6.581. Int J Mol Med. 2001. PMID: 11351269 Review.
Cited by
-
Structural insights into lethal contractural syndrome type 3 (LCCS3) caused by a missense mutation of PIP5Kγ.Biochem J. 2018 Jul 26;475(14):2257-2269. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20180326. Biochem J. 2018. PMID: 29959184 Free PMC article.
-
Localization of PIP5Kγ selectively in proprioceptive peripheral fields and also in sensory ganglionic satellite cells as well as neuronal cell membranes and their central terminals.J Anat. 2021 Nov;239(5):1196-1206. doi: 10.1111/joa.13491. Epub 2021 Jun 20. J Anat. 2021. PMID: 34151437 Free PMC article.
-
Mutations in Subunits of the Activating Signal Cointegrator 1 Complex Are Associated with Prenatal Spinal Muscular Atrophy and Congenital Bone Fractures.Am J Hum Genet. 2016 Mar 3;98(3):473-489. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2016.01.006. Epub 2016 Feb 25. Am J Hum Genet. 2016. PMID: 26924529 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and Analysis of the Expression of the PIP5K Gene Family in Tomatoes.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 21;25(1):159. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010159. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38203328 Free PMC article.
-
The Hidden Conundrum of Phosphoinositide Signaling in Cancer.Trends Cancer. 2016 Jul;2(7):378-390. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2016.05.009. Epub 2016 Jun 20. Trends Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27819060 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Web Resources
-
- GenBank, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Genbank/ (for PIP5K1C [accession number NM_012398])
-
- Map Viewer, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/mapview/ (for build 36)
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for AMCN, ARC, LCCS, and LCCS2)
-
- Primer3, http://www.genome.wi.mit.edu/cgi-bin/primer/primer3.cgi (for primer design)
References
-
- Pakkasjarvi N, Ritvanen A, Herva R, Peltonen L, Kestila M, Ignatius J (2006) Lethal congenital contracture syndrome (LCCS) and other lethal arthrogryposes in Finland—an epidemiological study. Am J Med Genet A 140:1834–1839 - PubMed
-
- Gissen P, Johnson CA, Morgan NV, Stapelbroek JM, Forshew T, Cooper WN, McKiernan PJ, Klomp LW, Morris AA, Wraith JE, et al (2004) Mutations in VPS33B, encoding a regulator of SNARE-dependent membrane fusion, cause arthrogryposis-renal dysfunction-cholestasis (ARC) syndrome. Nat Genet 36:400–40410.1038/ng1325 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

