Mutations in PRPS1, which encodes the phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate synthetase enzyme critical for nucleotide biosynthesis, cause hereditary peripheral neuropathy with hearing loss and optic neuropathy (cmtx5)
- PMID: 17701900
- PMCID: PMC1950833
- DOI: 10.1086/519529
Mutations in PRPS1, which encodes the phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate synthetase enzyme critical for nucleotide biosynthesis, cause hereditary peripheral neuropathy with hearing loss and optic neuropathy (cmtx5)
Abstract
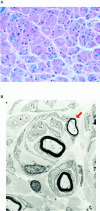
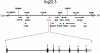
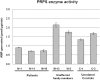
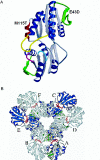
We have identified missense mutations at conserved amino acids in the PRPS1 gene on Xq22.3 in two families with a syndromic form of inherited peripheral neuropathy, one of Asian and one of European descent. The disease is inherited in an X-linked recessive manner, and the affected male patients invariably develop sensorineural hearing loss of prelingual type followed by gating disturbance and visual loss. The family of European descent was reported in 1967 as having Rosenberg-Chutorian syndrome, and recently a Korean family with the same symptom triad was identified with a novel disease locus CMTX5 on the chromosome band Xq21.32-q24. PRPS1 (phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate synthetase 1) is an isoform of the PRPS gene family and is ubiquitously expressed in human tissues, including cochlea. The enzyme mediates the biochemical step critical for purine metabolism and nucleotide biosynthesis. The mutations identified were E43D, in patients with Rosenberg-Chutorian syndrome, and M115T, in the Korean patients with CMTX5. We also showed decreased enzyme activity in patients with M115T. PRPS1 is the first CMT gene that encodes a metabolic enzyme, shedding a new light on the understanding of peripheral nerve-specific metabolism and also suggesting the potential of PRPS1 as a target for drugs in prevention and treatment of peripheral neuropathy by antimetabolite therapy.
Figures


References
Web Resources
-
- ClustalW, http://www.ebi.ac.uk/clustalw/
-
- GenBank, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Genbank/ (for PRPS1 [accession number NM_002764])
-
- Morton Lab Web site, http://www.brighamandwomens.org/bwh_hearing/ (for cochlear expression database)
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

