Crosstalk at the initial encounter: interplay between host defense and ameba survival strategies
- PMID: 17702556
- PMCID: PMC2679172
- DOI: 10.1016/j.coi.2007.07.005
Crosstalk at the initial encounter: interplay between host defense and ameba survival strategies
Abstract
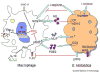
The host-parasite relationship is based on a series of interplays between host defense mechanisms and parasite survival strategies. Progress has been made in understanding the role of host immune response in amebiasis. While host cells elaborate diverse mechanisms for pathogen expulsion, amebae have also developed complex strategies to modulate host immune response and facilitate their own survival. This paper will give an overview of current research on the mutual interactions between host and Entamoeba histolytica in human and experimental amebiasis. Understanding this crosstalk is crucial for the effective design and implementation of new vaccines and drugs for this leading parasitic disease.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The immunopathogenesis of Entamoeba histolytica.Exp Parasitol. 2010 Nov;126(3):366-80. doi: 10.1016/j.exppara.2010.03.005. Epub 2010 Mar 19. Exp Parasitol. 2010. PMID: 20303955 Review.
-
Host-pathogen interaction in amebiasis and progress in vaccine development.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1998 Sep;17(9):601-14. doi: 10.1007/BF01708342. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1998. PMID: 9832261 Review.
-
Amebiasis now.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1989 Sep;41(3 Suppl):40-8. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1989.41.40. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1989. PMID: 2552852 Review. No abstract available.
-
Immune phenomena in amebiasis.Surv Immunol Res. 1984;3(1):1-10. doi: 10.1007/BF02918589. Surv Immunol Res. 1984. PMID: 6326234 Review. No abstract available.
-
Microbes and microbial toxins: paradigms for microbial-mucosal interactions. VI. Entamoeba histolytica: parasite-host interactions.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2001 Jun;280(6):G1049-54. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.2001.280.6.G1049. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11352795 Review.
Cited by
-
TNFα-mediated liver destruction by Kupffer cells and Ly6Chi monocytes during Entamoeba histolytica infection.PLoS Pathog. 2013 Jan;9(1):e1003096. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003096. Epub 2013 Jan 3. PLoS Pathog. 2013. PMID: 23300453 Free PMC article.
-
Entamoeba lysyl-tRNA synthetase contains a cytokine-like domain with chemokine activity towards human endothelial cells.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2011 Nov;5(11):e1398. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0001398. Epub 2011 Nov 29. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2011. PMID: 22140588 Free PMC article.
-
A review of the proposed role of neutrophils in rodent amebic liver abscess models.Parasite. 2016;23:6. doi: 10.1051/parasite/2016006. Epub 2016 Feb 15. Parasite. 2016. PMID: 26880421 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Entamoeba moshkovskii is associated with diarrhea in infants and causes diarrhea and colitis in mice.J Infect Dis. 2012 Sep 1;206(5):744-51. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jis414. Epub 2012 Jun 21. J Infect Dis. 2012. PMID: 22723640 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Entamoeba histolytica intermediate subunit lectin-specific human monoclonal antibodies generated in transgenic mice expressing human immunoglobulin loci.Infect Immun. 2009 Jan;77(1):549-56. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01002-08. Epub 2008 Nov 10. Infect Immun. 2009. PMID: 19001071 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO. Amoebiasis, WHO Weekly Epidemiologic Record. 1997;72:97–100.
-
- Haque R, Ali IKM, Sack RB, Ramakrishnan G, Farr BM, Petri WA., Jr Amebiasis and mucosal IgA antibody against the Entamoeba histolytica adherence lectin in Bangladeshi children. J Infect Dis. 2001;183:1787–1793. - PubMed
-
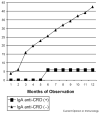
- Haque R, Mondal D, Duggal P, Kabir M, Roy S, Farr BM, Sack RB, Petri WA., Jr Entamoeba histolytica Infection in Children and Protection from Subsequent Amebiasis. Infect Immun. 2006;74:904–909. (Conclusions were drawn from a 4-year prospective study that immunity to amebic diarrhea and colitis exists; protection from amebiasis was associated with a stool anti-CRD IgA response.) - PMC - PubMed
-
- Caballero-Salcedo A, Viveros-Rogel M, Salvatierra B, Tapia-Conyer R, Sepulveda-Amor J, Gutierrez G, Ortiz-Ortiz L. Seroepidemiology of amebiasis in Mexico. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1994;50:412–419. - PubMed
-
- Ravidin JI, Stauffer WM. Entamoeba histolytica (Amebiasis) Infectious Disease and Their Etiologic Agents. 2004;270:3097–3111.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

