Molecular basis for HEF1/NEDD9/Cas-L action as a multifunctional co-ordinator of invasion, apoptosis and cell cycle
- PMID: 17703068
- PMCID: PMC1976382
- DOI: 10.1007/s12013-007-0036-3
Molecular basis for HEF1/NEDD9/Cas-L action as a multifunctional co-ordinator of invasion, apoptosis and cell cycle
Abstract
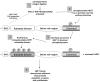
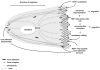
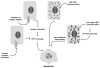
Upregulation of the scaffolding protein HEF1, also known as NEDD9 and Cas-L, has recently been identified as a pro-metastatic stimulus in a number of different solid tumors, and has also been strongly associated with pathogenesis of BCR-Abl-dependent tumors. As the evidence mounts for HEF1/NEDD9/Cas-L as a key player in metastatic cancer, it is timely to review the molecular regulation of HEF1/NEDD9/Cas-L. Most of the mortality associated with cancer arises from uncontrolled metastases, thus a better understanding of the properties of proteins specifically associated with promotion of this process may yield insights that improve cancer diagnosis and treatment. In this review, we summarize the extensive literature regarding HEF1/NEDD9/Cas-L expression and function in signaling relevant to cell attachment, migration, invasion, cell cycle, apoptosis, and oncogenic signal transduction. The complex function of HEF1/NEDD9/Cas-L revealed by this analysis leads us to propose a model in which alleviation of cell cycle checkpoints and acquired resistance to apoptosis is permissive for a HEF1/NEDD9/Cas-L-promoted pro-metastatic phenotype.
Figures

References
-
- Natarajan M, Stewart JE, Golemis EA, Pugacheva EN, Alexandropoulos K, Cox BD, Wang W, Grammer JR, Gladson CL. HEF1/NEDD9/CAS-L is a necessary and specific downstream effector of FAK that promotes the migration of glioblastoma cells. Oncogene. 2006;25:1721–32. - PubMed
-
- Kim M, Gans JD, Nogueira C, Wang A, Paik JH, Feng B, Brennan C, Hahn WC, Cordon-Cardo C, Wagner SN, Flotte TJ, Duncan LM, Granter SR, Chin L. Comparative oncogenomics identifies NEDD9 as a melanoma metastasis gene. Cell. 2006;125:1269–81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

