Integrating physical and genetic maps: from genomes to interaction networks
- PMID: 17703239
- PMCID: PMC2811081
- DOI: 10.1038/nrg2144
Integrating physical and genetic maps: from genomes to interaction networks
Abstract
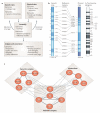
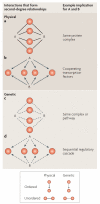
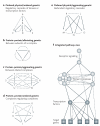
Physical and genetic mapping data have become as important to network biology as they once were to the Human Genome Project. Integrating physical and genetic networks currently faces several challenges: increasing the coverage of each type of network; establishing methods to assemble individual interaction measurements into contiguous pathway models; and annotating these pathways with detailed functional information. A particular challenge involves reconciling the wide variety of interaction types that are currently available. For this purpose, recent studies have sought to classify genetic and physical interactions along several complementary dimensions, such as ordered versus unordered, alleviating versus aggravating, and first versus second degree.
Figures

References
-
- Yu A, et al. Comparison of human genetic and sequence-based physical maps. Nature. 2001;409:951–953. - PubMed
-
- Sturtevant AH. The linear arrangement of six sex-linked factors in Drosophila, as shown by their mode of association. J. Exp. Zool. 1913;14:43–59.
-
- Goss SJ, Harris H. New method for mapping genes in human chromosomes. Nature. 1975;255:680–684. - PubMed
-
- Cox DR, Burmeister M, Price ER, Kim S, Myers RM. Radiation hybrid mapping: a somatic cell genetic method for constructing high-resolution maps of mammalian chromosomes. Science. 1990;250:245–250. - PubMed
-
- Fauth C, Speicher MR. Classifying by colors: FISH-based genome analysis. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 2001;93:1–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

