Control of lymphocyte infiltration of lung tumors in mice by host's genes: mapping of four Lynf (lymphocyte infiltration) loci
- PMID: 17703301
- PMCID: PMC11030561
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-007-0367-3
Control of lymphocyte infiltration of lung tumors in mice by host's genes: mapping of four Lynf (lymphocyte infiltration) loci
Abstract
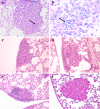
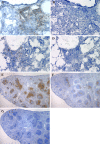
Tumor infiltration by lymphocytes is essential for cell-mediated immune elimination of tumors in experimental systems and in immunotherapy of cancer. Presence of lymphocytes in several human cancers has been associated with a better prognosis. We present evidence that individual propensity to tumor infiltration is genetically controlled. Infiltrating lymphocytes are present in 50% of lung tumors in O20/A mice, but in only 10% of lung tumors in OcB-9/Dem mice. This difference has been consistent in experiments conducted over 8 years in two different animal facilities. To test whether this strain difference is controlled genetically, we analyzed the presence of infiltrating lymphocytes in N-ethyl-N-nitroso-urea (ENU) induced lung tumors in (O20 x OcB-9) F(2) hybrids. We mapped four genetic loci, Lynf1 (Lymphocyte infiltration 1), Lynf2, Lynf3, and Lynf4 that significantly modify the presence and intensity of intra-tumoral infiltrates containing CD4(+) and CD8(+) T lymphocytes. These loci appear to be distinct from the genes encoding the molecules that are presently implicated in lymphocyte infiltration. Our findings open a novel approach for the assessment of individual propensity for tumor infiltration by genotyping the genes of the host that influence this process using DNA from any normal tissue. Such prediction of probability of tumor infiltration in individual cancer patients could help considerably to assess their prognosis and to decide about the application and the type of immunotherapy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Loci controlling lymphocyte production of interferon c after alloantigen stimulation in vitro and their co-localization with genes controlling lymphocyte infiltration of tumors and tumor susceptibility.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2010 Feb;59(2):203-13. doi: 10.1007/s00262-009-0739-y. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2010. PMID: 19655140 Free PMC article.
-
Lung tumor location and lymphocyte infiltration in mice are genetically determined.Exp Lung Res. 2005 Jun;31(5):513-25. doi: 10.1080/01902140590918740. Exp Lung Res. 2005. PMID: 16019985
-
Prognostic effect of epithelial and stromal lymphocyte infiltration in non-small cell lung cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2008 Aug 15;14(16):5220-7. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-0133. Clin Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 18698040
-
CD4 T cells inhibit in vivo the CD8-mediated immune response against murine colon carcinoma cells transduced with interleukin-12 genes.Eur J Immunol. 1995 Jan;25(1):137-46. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830250124. Eur J Immunol. 1995. PMID: 7843224
-
Inflammatory cell infiltration of tumors: Jekyll or Hyde.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2007 Dec;26(3-4):373-400. doi: 10.1007/s10555-007-9072-0. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2007. PMID: 17717638 Review.
Cited by
-
A locus on chromosome 8 controlling tumor regionality-a new type of tumor diversity in the mouse lung.Int J Cancer. 2010 Jun 1;126(11):2603-13. doi: 10.1002/ijc.24983. Int J Cancer. 2010. PMID: 19847808 Free PMC article.
-
Most lung and colon cancer susceptibility genes are pair-wise linked in mice, humans and rats.PLoS One. 2011 Feb 24;6(2):e14727. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0014727. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21390212 Free PMC article.
-
Loci controlling lymphocyte production of interferon c after alloantigen stimulation in vitro and their co-localization with genes controlling lymphocyte infiltration of tumors and tumor susceptibility.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2010 Feb;59(2):203-13. doi: 10.1007/s00262-009-0739-y. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2010. PMID: 19655140 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ganss R, Hanahan D. Tumor microenvironment can restrict the effectiveness of activated antitumor lymphocytes. Cancer Res. 1998;58:4673–4681. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

