Is the fixed-dose combination of telmisartan and hydrochlorothiazide a good approach to treat hypertension?
- PMID: 17703634
- PMCID: PMC2293961
Is the fixed-dose combination of telmisartan and hydrochlorothiazide a good approach to treat hypertension?
Abstract
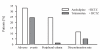
Blockade of the renin-angiotensin system with selective AT1 receptor antagonists is recognized as an effective mean to lower blood pressure in hypertensive patients. Among the class of AT1 receptor antagonists, telmisartan offers the advantage of a very long half-life. This enables blood pressure control over 24 hours using once-daily administration. The combination of telmisartan with hydrochlorothiazide is a logical step because numerous previous studies have demonstrated that sodium depletion enhances the antihypertensive efficacy of drugs interfering with the activity of the renin-angiotensin system (RAS). In accordance with past experience using similar compounds blocking the RAS, several controlled studies have now demonstrated that the fixed-dose combination oftelmisartan/hydrochlorothiazide is superior in lowering blood pressure than either telmisartan or hydrochlorothiazide alone. Of clinical interest also is the observation that the excellent clinical tolerance of the angiotensin II receptor antagonist is not affected by the association of the low-dose thiazide. Thus telmisartan/hydrochlorothiazide is an effective and well-tolerated antihypertensive combination. Finally, the development of fixed-dose combinations should improve drug adherence because of the one-pill-a-day regimen.
Figures

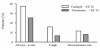
References
-
- Almansa C, Gomez LA, de Arriba AF, et al. Diphenypropionic acids as new AT-1 selective angiotensin II antagonists. J Med Chem. 1996;39:2197–206. - PubMed
-
- Bangalore, Kamalakkannan, Panjrath, et al. Fixed-dose combination improves medication compliance: a meta analysis [abstract] J Clin Hyper. 2006;8:A71.
-
- Barnett AH, Bain SC, Bouter P, et al. Angiotensin-receptor blockade versus converting-enzyme inhibition in type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:1952–61. - PubMed
-
- Battershill AJ, Scott LJ. Telmisartan: a review of its use in the management of hypertension. Drugs. 2006;66:51–83. - PubMed
-
- Beermann B, Groschinsky-Grind M. Pharmacokinetics of hydrochlorothiazide in man. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1977;12:297–303. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

