Metoprolol succinate extended release/hydrochlorothiazide combination tablets
- PMID: 17703635
- PMCID: PMC2293963
Metoprolol succinate extended release/hydrochlorothiazide combination tablets
Abstract
Lowering elevated blood pressure (BP) with drug therapy reduces the risk for catastrophic fatal and nonfatal cardiovascular events such as stroke and myocardial infarction. Given the heterogeneity of hypertension as a disease, the marked variability in an individual patient's BP response, and low response rates with monotherapy, expert groups such as the Joint National Committee (JNC) emphasize the value of combination antihypertensive regimens, noting that combinations, usually of different classes, have additive antihypertensive effects. Metoprolol succinate extended-release tablet is a beta-1 (cardio-selective) adrenoceptor-blocking agent formulated to provide controlled and predictable release of metoprolol. Hydrochlorothiazide (HCT) is a well-established diuretic and antihypertensive agent, which promotes natruresis by acting on the distal renal tubule. The pharmacokinetics, efficacy, and safety/tolerability of the antihypertensive combination tablet, metoprolol extended release hydrochlorothiazide, essentially reflect the well-described independent characteristics of each of the component agents. Not only is the combination product more effective than monotherapy with the individual components but the combination product allows a low-dose multidrug regimen as an alternative to high-dose monotherapy, thereby, minimizing the likelihood of dose-related side-effects.
Figures
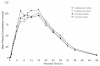
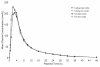
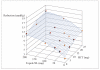
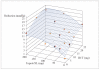
References
-
- ALLHAT Officers and Coordinators for the ALLHAT Collaborative Research Group. Major outcomes in high-risk hypertensive patients randomized to angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor or calcium channel blocker vs diuretic. JAMA. 2002;288:2981–97. - PubMed
-
- Bakris GL, Fonseca V, Katholi RE, et al. Metabolic effects of carvedilol vs metoprolol in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and hypertension. JAMA. 2004;292:2227–36. - PubMed
-
- Beermann B, Groschinsky-Grind M, Rosen A. Absorption, metabolism, and excretion of hydrochlorothiazide. Clin Pharmacol and Thera. 1976;19:531–7. - PubMed
-
- Dahlof B, Lindholm LH, Hansson L, et al. Morbidity and mortality in the Swedish trial in old patients with hypertension (STOP-hypertension) Lancet. 1991;338:1281–5. - PubMed
-
- Darmansjah I, Wong E, Setiawati A, et al. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties of controlled release (CR/ZOK) metoprolol in healthy Oriental subjects: a comparison with conventional formulations of metoprolol and atenolol. J Clin Pharmacol. 1990;30:S39–S45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

