Influence of the hydrodynamic environment on quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms
- PMID: 17704224
- PMCID: PMC2168657
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.01040-07
Influence of the hydrodynamic environment on quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms
Abstract
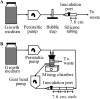
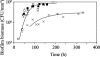
We provide experimental and modeling evidence that the hydrodynamic environment can impact quorum sensing (QS) in a Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm. The amount of biofilm biomass required for full QS induction of the population increased as the flow rate increased.
Figures



References
-
- Characklis, W. G. 1980. Biofilm development and destruction. Final report EPRI CS-1554. Electric Power Research Institute, Palo Alto, CA.
-
- Chopp, D. L., M. J. Kirisits, B. Moran, and M. R. Parsek. 2003. The dependence of quorum sensing on the depth of a growing biofilm. Bull. Math. Biol. 65:1053-1079. - PubMed
-
- Chopp, D. L., M. J. Kirisits, B. Moran, and M. R. Parsek. 2002. A mathematical model of quorum sensing in a growing bacterial biofilm. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 29:339-346. - PubMed
-
- Costerton, J. W., P. S. Stewart, and E. P. Greenberg. 1999. Bacterial biofilms: a common cause of persistent infections. Science 284:1318-1322. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

