The cardioprotection of the late phase of ischemic preconditioning is enhanced by postconditioning via a COX-2-mediated mechanism in conscious rats
- PMID: 17704286
- PMCID: PMC3713472
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00858.2007
The cardioprotection of the late phase of ischemic preconditioning is enhanced by postconditioning via a COX-2-mediated mechanism in conscious rats
Abstract
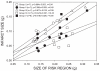
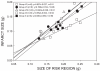
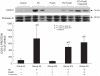
The present study sought to determine whether the combination of late preconditioning (PC) with postconditioning enhances the reduction in infarct size. Chronically instrumented rats were assigned to a 45-min (subset 1) or 60-min (subset 2) coronary occlusion followed by 24 h of reperfusion. In each subset, rats received no further intervention (control) or were preconditioned 24 h before occlusion (PC), postconditioned at the onset of reperfusion following occlusion, or preconditioned and postconditioned without (PC + postconditioning) or with the COX-2 inhibitor celecoxib (3 mg/kg ip; PC + postconditioning + celecoxib) 10 min before postconditioning. Myocardial cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) protein expression and COX-2 activity (assessed as myocardial levels of PGE(2)) were measured 6 min after reperfusion in an additional five groups (control, PC, postconditioning, PC + postconditioning, and PC + postconditioning + celecoxib) subjected to a 45-min occlusion. PC alone reduced infarct size after a 45-min occlusion but not after a 60-min occlusion. Postconditioning alone did not reduce infarct size in either setting. However, the combination of late PC and postconditioning resulted in a robust infarct-sparing effect in both settings, suggesting additive cardioprotection. Celecoxib completely abrogated the infarct-sparing effect of the combined interventions in both settings. Late PC increased COX-2 protein expression and PGE(2) content. PGE(2) content (but not COX-2 protein) was further increased by the combination of both interventions, suggesting that postconditioning increases the activity of COX-2 induced by late PC. In conclusion, the combination of late PC and postconditioning produces additive protection, likely due to a postconditioning-induced enhancement of COX-2 activity.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Cyclooxygenase-2 mediates the cardioprotective effects of the late phase of ischemic preconditioning in conscious rabbits.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Aug 29;97(18):10197-202. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.18.10197. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. PMID: 10963682 Free PMC article.
-
Cardioprotection by postconditioning in conscious rats is limited to coronary occlusions <45 min.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2006 Nov;291(5):H2308-17. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00479.2006. Epub 2006 Jun 30. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16815986 Free PMC article.
-
Isoflurane produces delayed preconditioning against myocardial ischemia and reperfusion injury: role of cyclooxygenase-2.Anesthesiology. 2004 Mar;100(3):525-31. doi: 10.1097/00000542-200403000-00010. Anesthesiology. 2004. PMID: 15108964
-
Discovery of a new function of cyclooxygenase (COX)-2: COX-2 is a cardioprotective protein that alleviates ischemia/reperfusion injury and mediates the late phase of preconditioning.Cardiovasc Res. 2002 Aug 15;55(3):506-19. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6363(02)00414-5. Cardiovasc Res. 2002. PMID: 12160947 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular basis of cardioprotection: signal transduction in ischemic pre-, post-, and remote conditioning.Circ Res. 2015 Feb 13;116(4):674-99. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.305348. Circ Res. 2015. PMID: 25677517 Review.
Cited by
-
The COX-2/PGI2 receptor axis plays an obligatory role in mediating the cardioprotection conferred by the late phase of ischemic preconditioning.PLoS One. 2012;7(7):e41178. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0041178. Epub 2012 Jul 23. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22844439 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation of modification of heart rate recovery with adaptation to myocardial ischemia in a model of sequential exercise testings.Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2008 Oct;13(4):364-70. doi: 10.1111/j.1542-474X.2008.00247.x. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2008. PMID: 18973493 Free PMC article.
-
Celecoxib reduces brain dopaminergic neuronaldysfunction, and improves sensorimotor behavioral performance in neonatal rats exposed to systemic lipopolysaccharide.J Neuroinflammation. 2013 Apr 5;10:45. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-10-45. J Neuroinflammation. 2013. PMID: 23561827 Free PMC article.
-
Celecoxib but not the combination of celecoxib+atorvastatin prevents the development of monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension in the rat.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2008 Sep;378(3):241-51. doi: 10.1007/s00210-008-0298-3. Epub 2008 Jun 10. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18542928
-
Galangin Resolves Cardiometabolic Disorders through Modulation of AdipoR1, COX-2, and NF-κB Expression in Rats Fed a High-Fat Diet.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 May 12;10(5):769. doi: 10.3390/antiox10050769. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34066039 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alcindor D, Krolikowski JG, Pagel PS, Warltier DC, Kersten JR. Cyclooxygenase-2 mediates ischemic, anesthetic, and pharmacologic preconditioning in vivo. Anesthesiology. 2004;100:547–554. - PubMed
-
- Argaud L, Gateau-Roesch O, Raisky O, Loufouat J, Robert D, Ovize M. Postconditioning inhibits mitochondrial permeability transition. Circulation. 2005;111:194–197. - PubMed
-
- Arnaud C, Joyeux-Faure M, Godin-Ribuot D, Ribuot C. COX-2: an in vivo evidence of its participation in heat stress-induced myocardial preconditioning. Cardiovasc Res. 2003;58:582–588. - PubMed
-
- Atar S, Ye Y, Lin Y, Freeberg SY, Nishi SP, Rosanio S, Huang MH, Uretsky BF, Perez-Polo JR, Birnbaum Y. Atorvastatin-induced cardioprotection is mediated by increasing inducible nitric oxide synthase and consequent S-nitrosylation of cyclooxygenase-2. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2006;290:H1960–H1968. - PubMed
-
- Bolli R. The late phase of preconditioning. Circ Res. 2000;87:972–983. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01-HL-55757/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL076794/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL055757/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL070897/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL-68088/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL078825/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL-70897/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL074351/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL-76794/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL-74351/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL-78825/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL068088/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

