The molecular mechanism of the inhibition by licofelone of the biosynthesis of 5-lipoxygenase products
- PMID: 17704828
- PMCID: PMC2050828
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707416
The molecular mechanism of the inhibition by licofelone of the biosynthesis of 5-lipoxygenase products
Abstract
Background and purpose: Licofelone is a dual inhibitor of the cyclooxygenase and 5-lipoxygenase (5-LO) pathway, and has been developed for the treatment of inflammatory diseases. Here, we investigated the molecular mechanisms underlying the inhibition by licofelone of the formation of 5-LO products.
Experimental approach: The efficacy of licofelone to inhibit the formation of 5-LO products was analysed in human isolated polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNL) or transfected HeLa cells, as well as in cell-free assays using respective cell homogenates or purified recombinant 5-LO. Moreover, the effects of licofelone on the subcellular redistribution of 5-LO were studied.
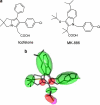
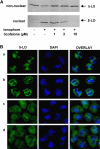
Key results: Licofelone potently blocked synthesis of 5-LO products in Ca(2+)-ionophore-activated PMNL (IC(50)=1.7 microM) but was a weak inhibitor of 5-LO activity in cell-free assays (IC(50)>>10 microM). The structures of licofelone and MK-886, an inhibitor of the 5-LO-activating protein (FLAP), were superimposable. The potencies of both licofelone and MK-886 in ionophore-activated PMNL were impaired upon increasing the concentration of arachidonic acid, or under conditions where 5-LO product formation was evoked by genotoxic, oxidative or hyperosmotic stress. Furthermore, licofelone prevented nuclear redistribution of 5-LO in ionophore-activated PMNL, as had been observed for FLAP inhibitors. Finally, licofelone as well as MK-886 caused only moderate inhibition of the synthesis of 5-LO products in HeLa cells, unless FLAP was co-transfected.
Conclusions and implications: Our data suggest that the potent inhibition of the biosynthesis of 5-LO products by licofelone requires an intact cellular environment and appears to be due to interference with FLAP.
Figures
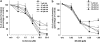

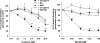

Similar articles
-
Phosphorylation- and stimulus-dependent inhibition of cellular 5-lipoxygenase activity by nonredox-type inhibitors.FASEB J. 2003 May;17(8):949-51. doi: 10.1096/fj.02-0815fje. Epub 2003 Mar 28. FASEB J. 2003. PMID: 12670876
-
BRP-187: A potent inhibitor of leukotriene biosynthesis that acts through impeding the dynamic 5-lipoxygenase/5-lipoxygenase-activating protein (FLAP) complex assembly.Biochem Pharmacol. 2016 Nov 1;119:17-26. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2016.08.023. Epub 2016 Aug 31. Biochem Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27592027
-
An experimental cell-based model for studying the cell biology and molecular pharmacology of 5-lipoxygenase-activating protein in leukotriene biosynthesis.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Sep;1840(9):2961-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2014.05.016. Epub 2014 Jun 4. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24905297
-
5-lipoxygenase and FLAP.Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2003 Aug-Sep;69(2-3):99-109. doi: 10.1016/s0952-3278(03)00070-x. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2003. PMID: 12895592 Review.
-
Recent advances in the search for novel 5-lipoxygenase inhibitors.Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2014 Jan;114(1):70-7. doi: 10.1111/bcpt.12114. Epub 2013 Sep 18. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2014. PMID: 23953428 Review.
Cited by
-
Synthesis, Biological Evaluation and Structure-Activity Relationships of Diflapolin Analogues as Dual sEH/FLAP Inhibitors.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2018 Nov 29;10(1):62-66. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.8b00415. eCollection 2019 Jan 10. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2018. PMID: 30655948 Free PMC article.
-
Androgen-mediated sex bias impairs efficiency of leukotriene biosynthesis inhibitors in males.J Clin Invest. 2017 Aug 1;127(8):3167-3176. doi: 10.1172/JCI92885. Epub 2017 Jul 24. J Clin Invest. 2017. PMID: 28737505 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological profile and efficiency in vivo of diflapolin, the first dual inhibitor of 5-lipoxygenase-activating protein and soluble epoxide hydrolase.Sci Rep. 2017 Aug 24;7(1):9398. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-09795-w. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28839250 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and structure-activity relationships for some novel diflapolin derivatives with benzimidazole subunit.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2022 Dec;37(1):1752-1764. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2022.2087645. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 36124840 Free PMC article.
-
2-(4-(Biphenyl-4-ylamino)-6-chloropyrimidin-2-ylthio)octanoic acid (HZ52)--a novel type of 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor with favourable molecular pharmacology and efficacy in vivo.Br J Pharmacol. 2011 Sep;164(2b):781-93. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01451.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21506958 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abramovitz M, Wong E, Cox ME, Richardson CD, Li C, Vickers PJ. 5-lipoxygenase-activating protein stimulates the utilization of arachidonic acid by 5-lipoxygenase. Eur J Biochem. 1993;215:105–111. - PubMed
-
- Brideau C, Chan C, Charleson S, Denis D, Evans JF, Ford-Hutchinson AW, et al. Pharmacology of MK-0591 (3-[1-(4-chlorobenzyl)-3-(t-butylthio)-5-(quinolin-2-yl-methoxy)-indol-2-yl]-2,2-dimethyl propanoic acid), a potent, orally active leukotriene biosynthesis inhibitor. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1992;70:799–807. - PubMed
-
- Brock TG, McNish RW, Bailie MB, Peters-Golden M. Rapid import of cytosolic 5-lipoxygenase into the nucleus of neutrophils after in vivo recruitment and in vitro adherence. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:8276–8280. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

