Thiamine diphosphate adenylyl transferase from E. coli: functional characterization of the enzyme synthesizing adenosine thiamine triphosphate
- PMID: 17705845
- PMCID: PMC1976097
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2091-8-17
Thiamine diphosphate adenylyl transferase from E. coli: functional characterization of the enzyme synthesizing adenosine thiamine triphosphate
Abstract
Background: We have recently identified a new thiamine derivative, adenosine thiamine triphosphate (AThTP), in E. coli. In intact bacteria, this nucleotide is synthesized only in the absence of a metabolizable carbon source and quickly disappears as soon as the cells receive a carbon source such as glucose. Thus, we hypothesized that AThTP may be a signal produced in response to carbon starvation.
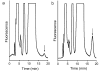
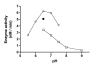
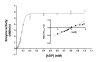
Results: Here we show that, in bacterial extracts, the biosynthesis of AThTP is carried out from thiamine diphosphate (ThDP) and ADP or ATP by a soluble high molecular mass nucleotidyl transferase. We partially purified this enzyme and characterized some of its functional properties. The enzyme activity had an absolute requirement for divalent metal ions, such as Mn2+ or Mg2+, as well as for a heat-stable soluble activator present in bacterial extracts. The enzyme has a pH optimum of 6.5-7.0 and a high Km for ThDP (5 mM), suggesting that, in vivo, the rate of AThTP synthesis is proportional to the free ThDP concentration. When ADP was used as the variable substrate at a fixed ThDP concentration, a sigmoid curve was obtained, with a Hill coefficient of 2.1 and an S0.5 value of 0.08 mM. The specificity of the AThTP synthesizing enzyme with respect to nucleotide substrate is restricted to ATP/ADP, and only ThDP can serve as the second substrate of the reaction. We tentatively named this enzyme ThDP adenylyl transferase (EC 2.7.7.65).
Conclusion: This is the first demonstration of an enzyme activity transferring a nucleotidyl group on thiamine diphosphate to produce AThTP. The existence of a mechanism for the enzymatic synthesis of this compound is in agreement with the hypothesis of a non-cofactor role for thiamine derivatives in living cells.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Adenosine thiamine triphosphate accumulates in Escherichia coli cells in response to specific conditions of metabolic stress.BMC Microbiol. 2010 May 21;10:148. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-10-148. BMC Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20492686 Free PMC article.
-
Thiamin diphosphate in biological chemistry: new aspects of thiamin metabolism, especially triphosphate derivatives acting other than as cofactors.FEBS J. 2009 Jun;276(11):2917-25. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2009.07019.x. Epub 2009 Apr 23. FEBS J. 2009. PMID: 19490098 Review.
-
Thiaminylated adenine nucleotides. Chemical synthesis, structural characterization and natural occurrence.FEBS J. 2009 Jun;276(12):3256-68. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2009.07040.x. Epub 2009 Apr 29. FEBS J. 2009. PMID: 19438713
-
Discovery of a natural thiamine adenine nucleotide.Nat Chem Biol. 2007 Apr;3(4):211-2. doi: 10.1038/nchembio867. Epub 2007 Mar 4. Nat Chem Biol. 2007. PMID: 17334376
-
Update on Thiamine Triphosphorylated Derivatives and Metabolizing Enzymatic Complexes.Biomolecules. 2021 Nov 7;11(11):1645. doi: 10.3390/biom11111645. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34827643 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Adenosine thiamine triphosphate accumulates in Escherichia coli cells in response to specific conditions of metabolic stress.BMC Microbiol. 2010 May 21;10:148. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-10-148. BMC Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20492686 Free PMC article.
-
Adenylate kinase-independent thiamine triphosphate accumulation under severe energy stress in Escherichia coli.BMC Microbiol. 2008 Jan 23;8:16. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-8-16. BMC Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18215312 Free PMC article.
-
Synthetic Thioesters of Thiamine: Promising Tools for Slowing Progression of Neurodegenerative Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 10;24(14):11296. doi: 10.3390/ijms241411296. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37511056 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An alternative role of FoF1-ATP synthase in Escherichia coli: synthesis of thiamine triphosphate.Sci Rep. 2013;3:1071. doi: 10.1038/srep01071. Epub 2013 Jan 15. Sci Rep. 2013. PMID: 23323214 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of 5'-Thiamine-Capped RNA.Molecules. 2020 Nov 24;25(23):5492. doi: 10.3390/molecules25235492. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33255222 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Enzyme Nomenclature http://www.expasy.ch/enzyme/
-
- Dawson EMC, Elliott DC, Elliott WH, Jones KM. Data for Biochemical Research. 3. Oxford: Oxford Science Publications; 1986.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

