Non-vesicular sterol transport in cells
- PMID: 17709145
- PMCID: PMC2078525
- DOI: 10.1016/j.plipres.2007.06.002
Non-vesicular sterol transport in cells
Abstract
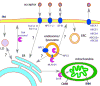
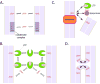
Sterols such as cholesterol are important components of cellular membranes. They are not uniformly distributed among organelles and maintaining the proper distribution of sterols is critical for many cellular functions. Both vesicular and non-vesicular pathways move sterols between membranes and into and out of cells. There is growing evidence that a number of non-vesicular transport pathways operate in cells and, in the past few years, a number of proteins have been proposed to facilitate this transfer. Some are soluble sterol transfer proteins that may move sterol between membranes. Others are integral membranes proteins that mediate sterol efflux, uptake from cells, and perhaps intracellular sterol transfer as well. In most cases, the mechanisms and regulation of these proteins remains poorly understood. This review summarizes our current knowledge of these proteins and how they could contribute to intracellular sterol trafficking and distribution.
Figures
References
-
- Yeagle PL. Cholesterol and the cell membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985;822:267–287. - PubMed
-
- Simons K, Ikonen E. How cells handle cholesterol. Science. 2000;290:1721–1726. - PubMed
-
- Ohvo-Rekila H, Ramstedt B, Leppimaki P, Slotte JP. Cholesterol interactions with phospholipids in membranes. Prog Lipid Res. 2002;41:66–97. - PubMed
-
- Sprong H, van der Sluijs P, van Meer G. How proteins move lipids and lipids move proteins. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2001;2:504–513. - PubMed
-
- Brown DA, London E. Structure and function of sphingolipid- and cholesterol-rich membrane rafts. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:17221–17224. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

