Molecular and epidemiological evidence for spread of multiresistant methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus strains in hospitals
- PMID: 17709473
- PMCID: PMC2167970
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01414-06
Molecular and epidemiological evidence for spread of multiresistant methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus strains in hospitals
Abstract
The excision of the staphylococcal chromosomal cassette mec (SCCmec) from methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) strains results in methicillin-susceptible S. aureus (MSSA) strains. In order to determine the proportion and diversity of multidrug-resistant MSSA (MR-MSSA) strains derived from MRSA strains, 247 mecA-negative isolates recovered in 60 French hospitals between 2002 and 2004 were characterized. The spa types of all strains were determined, and a subset of the strains (n = 30) was further genotyped by multilocus sequence typing. The IDI-MRSA assay was used to test the isolates for the presence of the SCCmec element, which was detected in 68% of all isolates analyzed. Molecular analysis of the samples suggested that 92% of the MR-MSSA isolates were derived from MRSA clones of diverse genetic backgrounds, of which the clone of sequence type 8 and SCCmec type IV(A) accounted for most of the samples. High variations in incidence data and differences in the molecular characteristics of the isolates from one hospital to another indicate that the emergence of MR-MSSA resulted from independent SCCmec excisions from epidemic MRSA isolates, as well as the diffusion of methicillin-susceptible strains after the loss of SCCmec. MR-MSSA could constitute a useful model for the study of the respective genetic and environmental factors involved in the dissemination of S. aureus in hospitals.
Figures

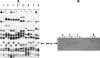

References
-
- Aires de Sousa, M., and H. de Lencastre. 2004. Bridges from hospitals to the laboratory: genetic portraits of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus clones. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 40:101-111. - PubMed
-
- Al-Haj-Hussein, B. T., M. A. Al-Shehri, E. A. Azhar, I. M. Ashankyty, and A. O. Osoba. 2005. Evaluation of two real-time PCR assays for the investigation of mecA gene in clinical isolates of MRSA in western Saudi Arabia. Saudi Med. J. 26:759-762. - PubMed
-
- Anonymous. 2006. Communiqué 2006. Comité de l'Antibiogramme de la Société Française de Microbiologie. http://www.sfm.asso.fr.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

