How gene order is influenced by the biophysics of transcription regulation
- PMID: 17709750
- PMCID: PMC1955771
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0700672104
How gene order is influenced by the biophysics of transcription regulation
Abstract
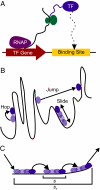
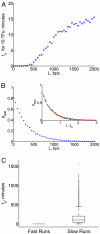
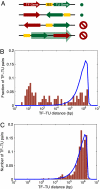
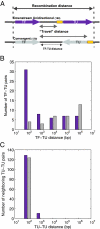
What are the forces that shape the structure of prokaryotic genomes: the order of genes, their proximity, and their orientation? Coregulation and coordinated horizontal gene transfer are believed to promote the proximity of functionally related genes and the formation of operons. However, forces that influence the structure of the genome beyond the level of a single operon remain unknown. Here, we show that the biophysical mechanism by which regulatory proteins search for their sites on DNA can impose constraints on genome structure. Using simulations, we demonstrate that rapid and reliable gene regulation requires that the transcription factor (TF) gene be close to the site on DNA the TF has to bind, thus promoting the colocalization of TF genes and their targets on the genome. We use parameters that have been measured in recent experiments to estimate the relevant length and times scales of this process and demonstrate that the search for a cognate site may be prohibitively slow if a TF has a low copy number and is not colocalized. We also analyze TFs and their sites in a number of bacterial genomes, confirm that they are colocalized significantly more often than expected, and show that this observation cannot be attributed to the pressure for coregulation or formation of selfish gene clusters, thus supporting the role of the biophysical constraint in shaping the structure of prokaryotic genomes. Our results demonstrate how spatial organization can influence timing and noise in gene expression.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The entire organization of transcription units on the Bacillus subtilis genome.BMC Genomics. 2007 Jun 28;8:197. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-8-197. BMC Genomics. 2007. PMID: 17598888 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling transcription regulatory networks by protein-DNA and protein-protein interaction mapping.Genome Res. 2006 Dec;16(12):1445-54. doi: 10.1101/gr.5321506. Epub 2006 Oct 19. Genome Res. 2006. PMID: 17053092 Review.
-
Genome-wide survey of transcription factors in prokaryotes reveals many bacteria-specific families not found in archaea.DNA Res. 2005;12(5):269-80. doi: 10.1093/dnares/dsi016. Epub 2006 Jan 10. DNA Res. 2005. PMID: 16769689
-
Persistence drives gene clustering in bacterial genomes.BMC Genomics. 2008 Jan 7;9:4. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-9-4. BMC Genomics. 2008. PMID: 18179692 Free PMC article.
-
DNA looping in gene regulation: from the assembly of macromolecular complexes to the control of transcriptional noise.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2005 Apr;15(2):136-44. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2005.02.005. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2005. PMID: 15797196 Review.
Cited by
-
Gene location and DNA density determine transcription factor distributions in Escherichia coli.Mol Syst Biol. 2012;8:610. doi: 10.1038/msb.2012.42. Mol Syst Biol. 2012. PMID: 22968444 Free PMC article.
-
Towards Conformation-Sensitive Inhibition of Gyrase: Implications of Mechanistic Insight for the Identification and Improvement of Inhibitors.Molecules. 2021 Feb 25;26(5):1234. doi: 10.3390/molecules26051234. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33669078 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Probing microscopic origins of confined subdiffusion by first-passage observables.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Apr 15;105(15):5675-80. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0712158105. Epub 2008 Apr 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18391208 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial effects on the speed and reliability of protein-DNA search.Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Jun;36(11):3570-8. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn173. Epub 2008 May 3. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008. PMID: 18453629 Free PMC article.
-
Sliding and jumping of single EcoRV restriction enzymes on non-cognate DNA.Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Jul;36(12):4118-27. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn376. Epub 2008 Jun 10. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008. PMID: 18544605 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pardee AB, Jacob F, Monod J. J Mol Biol. 1959;1:165–178.
-
- Warren PB, ten Wolde PR. J Mol Biol. 2004;342:1379–1390. - PubMed
-
- Korbel JO, Jensen LJ, von Mering C, Bork P. Nat Biotechnol. 2004;22:911–917. - PubMed
-
- Kepes F. J Mol Biol. 2004;340:957–964. - PubMed
-
- Hershberg R, Yeger-Lotem E, Margalit H. Trends Genet. 2005;21:138–142. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

