Noise and poise: Enhancement of postural complexity in the elderly with a stochastic-resonance-based therapy
- PMID: 17710211
- PMCID: PMC1949396
- DOI: 10.1209/0295-5075/77/68008
Noise and poise: Enhancement of postural complexity in the elderly with a stochastic-resonance-based therapy
Abstract
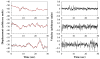
Pathologic states are associated with a loss of dynamical complexity. Therefore, therapeutic interventions that increase physiologic complexity may enhance health status. Using multiscale entropy analysis, we show that the postural sway dynamics of healthy young and healthy elderly subjects are more complex than that of elderly subjects with a history of falls. Application of subsensory noise to the feet has been demonstrated to improve postural stability in the elderly. We next show that this therapy significantly increases the multiscale complexity of sway fluctuations in healthy elderly subjects. Quantification of changes in dynamical complexity of biologic variability may be the basis of a new approach to assessing risk and to predicting the efficacy of clinical interventions, including noise-based therapies.
Figures
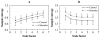
References
-
- Lipsitz LA, Jonsson PV, Kelley MM, Koestner JS. J Gerontol. 1991;46:M114. - PubMed
-
- Sattin RW. Annu Rev Pub Health. 1992;13:489. - PubMed
-
- Simoneau GG, et al. Diabetes Care. 1994;17:1411. - PubMed
-
- Mitchell SL, Collins JJ, De Luca CJ, Burrows A, Lipsitz LA. Neurosci Lett. 1995;197:133. - PubMed
-
- Miyai I, Mauricio RL, Reding MJ. J Neurol Rehabil. 1997;11:35.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
