Piracetam improves cognitive deficits caused by chronic cerebral hypoperfusion in rats
- PMID: 17710536
- PMCID: PMC11514981
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-007-9165-x
Piracetam improves cognitive deficits caused by chronic cerebral hypoperfusion in rats
Abstract
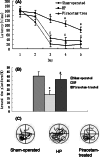
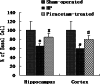
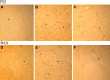
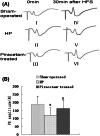
Piracetam is the derivate of gamma-aminobutyric acid, which improves the cognition,memory,consciousness, and is widely applied in the clinical treatment of brain dysfunction. In the present experiments, we study the effects of piracetam on chronic cerebral hypoperfused rats and observe its influence on amino acids, synaptic plasticity in the Perforant path-CA3 pathway and apoptosis in vivo. Cerebral hypoperfusion for 30 days by occlusion of bilateral common carotid arteries induced marked amnesic effects along with neuron damage, including: (1) spatial learning and memory deficits shown by longer escape latency and shorter time spent in the target quadrant; (2) significant neuronal loss and nuclei condensation in the cortex and hippocampus especially in CA1 region; (3) lower induction rate of long term potentiation, overexpression of BAX and P53 protein, and lower content of excitatory and inhibitory amino acids in hippocampus. Oral administration of piracetam (600 mg/kg, once per day for 30 days) markedly improved the memory impairment, increased the amino acid content in hippocampus, and attenuated neuronal damage. The ability of piracetam to attenuate memory deficits and neuronal damage after hypoperfusion may be beneficial in cerebrovascular type dementia.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Effects of amelioration of total flavonoids from stems and leaves of Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi on cognitive deficits, neuronal damage and free radicals disorder induced by cerebral ischemia in rats.Biol Pharm Bull. 2006 Apr;29(4):805-10. doi: 10.1248/bpb.29.805. Biol Pharm Bull. 2006. PMID: 16595923
-
Therapeutic benefit of Yangxue Qingnao Granule on cognitive impairment induced by chronic cerebral hypoperfusion in rats.Chin J Integr Med. 2011 Feb;17(2):134-40. doi: 10.1007/s11655-011-0643-0. Epub 2011 Mar 9. Chin J Integr Med. 2011. PMID: 21390580
-
Centrophenoxine improves chronic cerebral ischemia induced cognitive deficit and neuronal degeneration in rats.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2004 Dec;25(12):1590-6. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2004. PMID: 15569402
-
Diabetes augments cognitive dysfunction in chronic cerebral hypoperfusion by increasing neuronal cell death: implication of cilostazol for diabetes mellitus-induced dementia.Neurobiol Dis. 2015 Jan;73:12-23. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2014.08.034. Epub 2014 Oct 2. Neurobiol Dis. 2015. PMID: 25281785
-
The mechanistic role of piracetam in the management of vascular dementia.Behav Brain Res. 2025 May 28;486:115551. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2025.115551. Epub 2025 Mar 24. Behav Brain Res. 2025. PMID: 40139397 Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmacology of stimulants prohibited by the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA).Br J Pharmacol. 2008 Jun;154(3):606-22. doi: 10.1038/bjp.2008.124. Br J Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18500382 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cure of Alzheimer's Dementia Requires Addressing All of the Affected Brain Cell Types.J Clin Med. 2023 Mar 4;12(5):2049. doi: 10.3390/jcm12052049. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 36902833 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the Effects of Citicoline and Piracetam on Hypoxic-ischemic Brain Damage in Neonatal Rabbits.Iran J Child Neurol. 2022 Winter;16(1):77-84. doi: 10.22037/ijcn.v15i4.29816. Epub 2022 Jan 1. Iran J Child Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35222659 Free PMC article.
-
Improved mitochondrial function in brain aging and Alzheimer disease - the new mechanism of action of the old metabolic enhancer piracetam.Front Neurosci. 2010 Sep 7;4:44. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2010.00044. eCollection 2010. Front Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20877425 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of leaf extract of Capparis zeylanica Linn. on spatial learning and memory in rats.J Nat Med. 2012 Oct;66(4):600-7. doi: 10.1007/s11418-012-0626-2. Epub 2012 Jan 20. J Nat Med. 2012. PMID: 22261859
References
-
- Berzhanskaya J, Urban NN, Barrionuevo G (1998) Electrophysiological and pharmacological characterization of the direct perforant path input to hippocampal area CA3. J Neurophysiol 79(4):2111–2118 - PubMed
-
- Bianchi L, Colivicchi MA, Bolan JP (1998) The release of amino acids from rat neostriatum and substantia nigra in vivo: an adult microdialysis probe analysis. Neuroscience 87(1):171–180 - PubMed
-
- Bliss TVP, Collingridge GL (1993) A synaptic model of memory: long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature 361(6407):31–39 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

