Neuroprotective mechanism of taurine due to up-regulating calpastatin and down-regulating calpain and caspase-3 during focal cerebral ischemia
- PMID: 17712625
- PMCID: PMC11515008
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-007-9183-8
Neuroprotective mechanism of taurine due to up-regulating calpastatin and down-regulating calpain and caspase-3 during focal cerebral ischemia
Abstract
Aims: Taurine as an endogenous substance possesses a number of cytoprotective properties. In the study, we have evaluated the neuroprotective effect of taurine and investigated whether taurine exerted neuroprotection through affecting calpain/calpastatin or caspase-3 actions during focal cerebral ischemia, since calpain and caspase-3 play central roles in ischemic neuronal death.
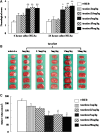
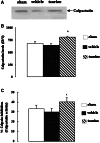
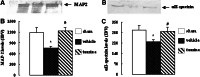
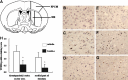
Methods: Male Sprague-Dawley rats were subjected to 2 h of middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAo), and 22 h of reperfusion. Taurine was administrated intravenously 1 h after MCAo. The dose-responses of taurine to MCAo were determined. Next, the effects of taurine on the activities of calpain, calpastatin and caspase-3, the levels of calpastatin, microtubule-associated protein-2 (MAP-2) and alphaII-spectrin, and the apoptotic cell death in penumbra were evaluated.
Results: Taurine reduced neurological deficits and decreased the infarct volume 24 h after MCAo in a dose-dependent manner. Treatment with 50 mg/kg of taurine significantly increased the calpastatin protein levels and activities, and markedly reduced the m-calpain and caspase-3 activities in penumbra 24 h after MCAo, however, it had no significant effect on mu-calpain activity. Moreover, taurine significantly increased the MAP-2 and alphaII-spectrin protein levels, and markedly reduced the ischemia-induced TUNEL staining positive score within penumbra 24 h after MCAo.
Conclusions: Our data demonstrate the dose-dependent neuroprotection of taurine against transient focal cerebral ischemia, and suggest that one of protective mechanisms of taurine against ischemia may be blocking the m-calpain and caspase-3-mediated apoptotic cell death pathways.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Cross-talk between calpain and caspase-3 in penumbra and core during focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2008 Jan;28(1):71-85. doi: 10.1007/s10571-007-9250-1. Epub 2007 Dec 21. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2008. PMID: 18157632 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of nNOS reduces ischemic cell death through down-regulating calpain and caspase-3 after experimental stroke.Neurochem Int. 2009 May-Jun;54(5-6):339-46. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2008.12.017. Epub 2008 Dec 31. Neurochem Int. 2009. PMID: 19162106
-
Neuroprotective actions of aminoguanidine involve reduced the activation of calpain and caspase-3 in a rat model of stroke.Neurochem Int. 2010 Mar;56(4):634-41. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2010.01.009. Epub 2010 Jan 29. Neurochem Int. 2010. PMID: 20116408
-
Protective effects of Tongxinluo on cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury related to Connexin 43/Calpain II/Bax/Caspase-3 pathway in rat.J Ethnopharmacol. 2017 Feb 23;198:148-157. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2017.01.004. Epub 2017 Jan 5. J Ethnopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28065778
-
Protective functions of taurine against experimental stroke through depressing mitochondria-mediated cell death in rats.Amino Acids. 2011 May;40(5):1419-29. doi: 10.1007/s00726-010-0751-8. Epub 2010 Sep 23. Amino Acids. 2011. PMID: 20862501
Cited by
-
Central Noradrenergic Agonists in the Treatment of Ischemic Stroke-an Overview.Transl Stroke Res. 2020 Apr;11(2):165-184. doi: 10.1007/s12975-019-00718-7. Epub 2019 Jul 20. Transl Stroke Res. 2020. PMID: 31327133 Review.
-
Caspase and calpain activation both contribute to sepsis-induced diaphragmatic weakness.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2009 Nov;107(5):1389-96. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00341.2009. Epub 2009 Aug 6. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2009. PMID: 19661453 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic taurine treatment provides neuroprotection against retinal photoreceptor degeneration and visual function impairments.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019 Aug 7;13:2689-2702. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S194169. eCollection 2019. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019. PMID: 31496648 Free PMC article.
-
Emergence of taurine as a therapeutic agent for neurological disorders.Neural Regen Res. 2024 Jan;19(1):62-68. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.374139. Neural Regen Res. 2024. PMID: 37488845 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Taurine Reduces tPA (Tissue-Type Plasminogen Activator)-Induced Hemorrhage and Microvascular Thrombosis After Embolic Stroke in Rat.Stroke. 2018 Jul;49(7):1708-1718. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.118.020747. Epub 2018 May 29. Stroke. 2018. PMID: 29844028 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ashwal S, Tone B, Tian HR, Cole DJ, Pearce WJ (1998) Core and penumbral nitric oxide synthase activity during cerebral ischemia and reperfusion. Stroke 29:1037–1047 - PubMed
-
- Bennett V (1990) Spectrin: a structural mediator between diverse plasma membrane proteins and the cytoplasm. Curr Opin Cell Biol 2:51–56 - PubMed
-
- Birdsall TC (1998) Therapeutic applications of taurine. Altern Med Rev 3:128–136 - PubMed
-
- Blomgren K, Hallin U, Andersson AL, Puka-Sundvall M, Bahr BA, McRae A, Saido TC, Kawashima S, Hagberg H (1999) Calpastatin is up-regulated in response to hypoxia and is a suicide substrate to calpain after neonatal cerebral hypoxia-ischemia. J Biol Chem 274:14046–14052 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

