Type-1 cannabinoid receptors colocalize with caveolin-1 in neuronal cells
- PMID: 17714745
- PMCID: PMC2706320
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2007.06.030
Type-1 cannabinoid receptors colocalize with caveolin-1 in neuronal cells
Abstract
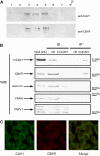
Type-1 (CB1) and type-2 (CB2) cannabinoid receptors belong to the rhodopsin family of G protein-coupled receptors, and are activated by endogenous lipids termed "endocannabinoids". Recent reports have demonstrated that CB1R, unlike CB2R and other receptors and metabolic enzymes of endocannabinoids, functions in the context of lipid rafts, i.e. plasma membrane microdomains which may be important in modulating signal transduction. Here, we present novel data based on cell subfractionation, immunoprecipitation and confocal microscopy studies, that show that in C6 cells CB1R co-localizes almost entirely with caveolin-1. We also show that trafficking of CB1R in response to the raft disruptor methyl-beta-cyclodextrin (MCD) is superimposable on that of caveolin-1, and that MCD treatment increases the accessibility of CB1R to its specific antibodies. These findings may be relevant for the manifold CB1R-dependent activities of endocannabinoids, like the regulation of apoptosis and of neurodegenerative diseases.
Figures


References
-
- Arcangeli A., Becchetti A. Complex functional interaction between integrin receptors and ion channels. Trends Cell Biol. 2006;16:631–639. - PubMed
-
- Bari M., Battista N., Fezza F., Finazzi-Agrò A., Maccarrone M. Lipid rafts control signaling of type-1 cannabinoid receptors in neuronal cells. Implications for anandamide-induced apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2005;280:12212–12220. - PubMed
-
- Bari M., Battista N., Fezza F., Gasperi V., Maccarrone M. New insights into endocannabinoid degradation and its therapeutic potential. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2006;6:257–268. - PubMed
-
- Bari M., Spagnuolo P., Fezza F., Oddi S., Pasquariello N., Finazzi-Agrò A., Maccarrone M. Effect of lipid rafts on CB2 receptor signaling and 2-arachidonoyl-glycerol metabolism in human immune cells. J. Immunol. 2006;177:4971–4980. - PubMed
-
- Barnett-Norris J., Lynch D., Reggio P.H. Lipids, lipid rafts and caveolae: their importance for GPCR signaling and their centrality to the endocannabinoid system. Life Sci. 2005;77:1625–1639. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

