Agmatine reduces balance deficits in a rat model of third trimester binge-like ethanol exposure
- PMID: 17714770
- PMCID: PMC2048752
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pbb.2007.07.012
Agmatine reduces balance deficits in a rat model of third trimester binge-like ethanol exposure
Abstract
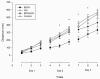
This study examined the effects of binge-like ethanol (ETOH) exposure in neonatal rats on a cerebellar-mediated balance task, and the ability of agmatine, an n-methyl-d-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) modulator, to reverse such effects. Five neonatal treatments groups were used, including ETOH (6.0 g/kg/day), AG (20 mg/kg), ETOH plus AG (6.0 g/kg/day and 20 mg/kg), a maltose control, and a non-treated control. Ethanol was administered via oral intubation twice daily for eight days, (AG was administered with the last ETOH intubation only). Two exposure periods were used; PND 1-8 or PND 8-15. On PND 31-33, balance performance on a single dowel was tested. Treatment with AG during withdrawal in ETOH exposed animals improved performance relative to ETOH alone among the PND 1-8 exposure period. ETOH exposure during the 2nd postnatal week did not impair balance. These findings provide further support that exposure to ETOH during critical developmental periods can impair performance on a cerebellar-dependent balance task. Of perhaps greater significance, co-administration of agmatine reduced these deficits suggesting that NMDA modulation via polyamine blockade may provide a novel approach to attenuating damage associated with binge-like ETOH consumption.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Agmatine reduces ultrasonic vocalization deficits in female rat pups exposed neonatally to ethanol.Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2010 Mar-Apr;32(2):158-63. doi: 10.1016/j.ntt.2009.11.005. Epub 2009 Nov 27. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2010. PMID: 19945529 Free PMC article.
-
Difluoromethylornithine (DFMO) reduces deficits in isolation-induced ultrasonic vocalizations and balance following neonatal ethanol exposure in rats.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2009 Mar;92(1):44-50. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2008.10.008. Epub 2008 Oct 25. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2009. PMID: 18992275 Free PMC article.
-
Repeated intermittent alcohol exposure during the third trimester-equivalent increases expression of the GABA(A) receptor δ subunit in cerebellar granule neurons and delays motor development in rats.Neuropharmacology. 2014 Apr;79:262-74. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.11.020. Epub 2013 Dec 4. Neuropharmacology. 2014. PMID: 24316160 Free PMC article.
-
Acute and long-term Purkinje cell loss following a single ethanol binge during the early third trimester equivalent in the rat.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2012 Aug;36(8):1365-73. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2012.01743.x. Epub 2012 Mar 8. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2012. PMID: 22404759
-
Administration of memantine during ethanol withdrawal in neonatal rats: effects on long-term ethanol-induced motor incoordination and cerebellar Purkinje cell loss.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2011 Feb;35(2):355-64. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2010.01351.x. Epub 2010 Nov 10. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2011. PMID: 21070252 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Prenatal choline supplementation mitigates behavioral alterations associated with prenatal alcohol exposure in rats.Birth Defects Res A Clin Mol Teratol. 2010 Oct;88(10):827-37. doi: 10.1002/bdra.20713. Birth Defects Res A Clin Mol Teratol. 2010. PMID: 20706995 Free PMC article.
-
Administration of memantine during withdrawal mitigates overactivity and spatial learning impairments associated with neonatal alcohol exposure in rats.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2014 Feb;38(2):529-37. doi: 10.1111/acer.12259. Epub 2014 Jan 15. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2014. PMID: 24428701 Free PMC article.
-
Behavioral deficits and cellular damage following developmental ethanol exposure in rats are attenuated by CP-101,606, an NMDAR antagonist with unique NR2B specificity.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2012 Jan;100(3):545-53. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2011.10.013. Epub 2011 Oct 20. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2012. PMID: 22037411 Free PMC article.
-
Recent breakthroughs in understanding the cerebellum's role in fetal alcohol spectrum disorder: A systematic review.Alcohol. 2024 Sep;119:37-71. doi: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2023.12.003. Epub 2023 Dec 13. Alcohol. 2024. PMID: 38097146
-
Fetal alcohol spectrum disorders: experimental treatments and strategies for intervention.Alcohol Res Health. 2011;34(1):76-85. Alcohol Res Health. 2011. PMID: 23580044 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abbey H, Howard E. Statistical procedure in developmental studies on species with multiple offspring. Dev Psychobiol. 1973;6:329–35. - PubMed
-
- Allgaier C. Ethanol sensitivity of NMDA receptors. Neurochem Int. 2002;41:377–82. - PubMed
-
- Champagne F, Meaney MJ. Like mother, like daughter: evidence for non-genomic transmission of parental behavior and stress responsivity. Prog Brain Res. 2001;133:287–302. - PubMed
-
- Chandler LJ, Norwood D, Sutton G. Chronic ethanol upregulates NMDA and AMPA, but not kainate receptor subunit proteins in rat primary cortical cultures. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1999;23:363–70. - PubMed
-
- Cull-Candy S, Brickley S, Farrant M. NMDA receptor subunits: diversity, development and disease. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2001;11:327–35. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

