Cooperation of NF-kappaB2/p100 activation and the PDZ domain binding motif signal in human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) Tax1 but not HTLV-2 Tax2 is crucial for interleukin-2-independent growth transformation of a T-cell line
- PMID: 17715223
- PMCID: PMC2168800
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00532-07
Cooperation of NF-kappaB2/p100 activation and the PDZ domain binding motif signal in human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) Tax1 but not HTLV-2 Tax2 is crucial for interleukin-2-independent growth transformation of a T-cell line
Abstract
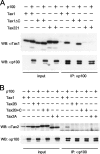
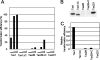
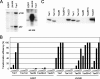
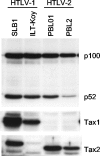
Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) but not HTLV-2 is associated with adult T-cell leukemia, and the distinct pathogenicity of these two closely related viruses is thought to stem from the distinct biological functions of the respective transforming proteins, HTLV-1 Tax1 and HTLV-2 Tax2. In this study, we demonstrate that Tax1 but not Tax2 interacts with NF-kappaB2/p100 and activates it by inducing the cleavage of p100 into the active transcription factor p52. Using RNA interference methods, we further show that NF-kappaB2/p100 is required for the transformation induced by Tax1, as determined by the ability to convert a T-cell line (CTLL-2) from interleukin-2 (IL-2)-dependent to -independent growth. While Tax2 shows a reduced transforming activity relative to Tax1, Tax2 fused with a PDZ domain binding motif (PBM) present only in Tax1 shows transforming activity equivalent to that of Tax1 in CTLL-2 cells expressing an inducer of p52 processing. These results reveal that the activation of NF-kappaB2/p100 plays a crucial role in the Tax1-mediated transformation of T cells and that NF-kappaB2/p100 activation and PBM function are both responsible for the augmented transforming activity of Tax1 relative to Tax2, thus suggesting that these Tax1-specific functions play crucial roles in HTLV-1 leukemogenesis.
Figures


References
-
- Akita, K., S. Kawata, and K. Shimotohno. 2005. p21WAF1 modulates NF-κB signaling and induces anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2 in Tax-expressing rat fibroblast. Virology 332:249-257. - PubMed
-
- Atkinson, P. G., H. J. Coope, M. Rowe, and S. C. Ley. 2003. Latent membrane protein 1 of Epstein-Barr virus stimulates processing of NF-kappa B2 p100 to p52. J. Biol. Chem. 278:51134-51142. - PubMed
-
- Cross, S. L., M. B. Feinberg, J. B. Wolf, N. J. Holbrook, F. Wong-Staal, and W. J. Leonard. 1987. Regulation of the human interleukin-2 receptor alpha chain promoter: activation of a nonfunctional promoter by the transactivator gene of HTLV-I. Cell 49:47-56. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

