Angiotensin II controls occludin function and is required for blood brain barrier maintenance: relevance to multiple sclerosis
- PMID: 17715340
- PMCID: PMC6672193
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2088-07.2007
Angiotensin II controls occludin function and is required for blood brain barrier maintenance: relevance to multiple sclerosis
Abstract
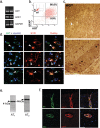
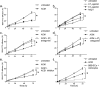
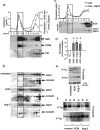
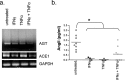
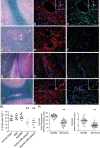
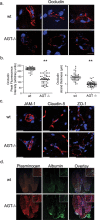
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) restricts molecular and cellular trafficking between the blood and the CNS. Although astrocytes are known to control BBB permeability, the molecular determinants of this effect remain unknown. We show that angiotensinogen (AGT) produced and secreted by astrocytes is cleaved into angiotensin II (AngII) and acts on type 1 angiotensin receptors (AT1) expressed by BBB endothelial cells (ECs). Activation of AT1 restricts the passage of molecular tracers across human BBB-derived ECs through threonine-phosphorylation of the tight junction protein occludin and its mobilization to lipid raft membrane microdomains. We also show that AGT knock-out animals have disorganized occludin strands at the level of the BBB and a diffuse accumulation of the endogenous serum protein plasminogen in the CNS, compared with wild-type animals. Finally, we demonstrate a reduction in the number of AGT-immunopositive perivascular astrocytes in multiple sclerosis (MS) lesions, which correlates with a reduced expression of occludin similarly seen in the CNS of AGT knock-out animals. Such a reduction in astrocyte-expressed AGT and AngII is dependent, in vitro, on the proinflammatory cytokines tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interferon-gamma. Our study defines a novel physiological role for AngII in the CNS and suggests that inflammation-induced downregulation of AngII production by astrocytes is involved in BBB dysfunction in MS lesions.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Statins reduce human blood-brain barrier permeability and restrict leukocyte migration: relevance to multiple sclerosis.Ann Neurol. 2006 Jul;60(1):45-55. doi: 10.1002/ana.20875. Ann Neurol. 2006. PMID: 16729291
-
Influence of basolateral condition on the regulation of brain microvascular endothelial tight junction properties and barrier function.Brain Res. 2008 Feb 8;1193:84-92. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2007.11.072. Epub 2007 Dec 14. Brain Res. 2008. PMID: 18177846
-
Differential susceptibility of cerebral and cerebellar murine brain microvascular endothelial cells to loss of barrier properties in response to inflammatory stimuli.J Neuroimmunol. 2006 Oct;179(1-2):37-45. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2006.06.019. Epub 2006 Aug 1. J Neuroimmunol. 2006. PMID: 16884785
-
Morphofunctional aspects of the blood-brain barrier.Curr Drug Metab. 2012 Jan;13(1):50-60. doi: 10.2174/138920012798356970. Curr Drug Metab. 2012. PMID: 22292807 Review.
-
Cellular elements of the blood-brain barrier.Neurochem Res. 2009 Dec;34(12):2067-77. doi: 10.1007/s11064-009-0081-y. Epub 2009 Oct 25. Neurochem Res. 2009. PMID: 19856206 Review.
Cited by
-
Transgenic animal models to explore and modulate the blood brain and blood retinal barriers of the CNS.Fluids Barriers CNS. 2022 Nov 1;19(1):86. doi: 10.1186/s12987-022-00386-0. Fluids Barriers CNS. 2022. PMID: 36320068 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functions of lipid raft membrane microdomains at the blood-brain barrier.J Mol Med (Berl). 2009 Aug;87(8):765-74. doi: 10.1007/s00109-009-0488-6. Epub 2009 May 30. J Mol Med (Berl). 2009. PMID: 19484210 Review.
-
Blockade of brain angiotensin II AT1 receptors ameliorates stress, anxiety, brain inflammation and ischemia: Therapeutic implications.Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2011 Jan;36(1):1-18. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2010.10.001. Epub 2010 Oct 29. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2011. PMID: 21035950 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pericytes are required for blood-brain barrier integrity during embryogenesis.Nature. 2010 Nov 25;468(7323):562-6. doi: 10.1038/nature09513. Epub 2010 Oct 13. Nature. 2010. PMID: 20944625 Free PMC article.
-
Ammonium perchlorate: serum dosimetry, neurotoxicity, and resilience of the neonatal rat thyroid system.Toxicol Sci. 2024 Feb 28;198(1):113-127. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfad133. Toxicol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38145495 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbott NJ, Ronnback L, Hansson E. Astrocyte-endothelial interactions at the blood–brain barrier. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2006;7:41–53. - PubMed
-
- Alter A, Duddy M, Hebert S, Biernacki K, Prat A, Antel JP, Yong VW, Nuttall RK, Pennington CJ, Edwards DR, Bar-Or A. Determinants of human B cell migration across brain endothelial cells. J Immunol. 2003;170:4497–4505. - PubMed
-
- Arthur FE, Shivers RR, Bowman PD. Astrocyte-mediated induction of tight junctions in brain capillary endothelium: an efficient in vitro model. Brain Res. 1987;433:155–159. - PubMed
-
- Biernacki K, Prat A, Blain M, Antel JP. Regulation of cellular and molecular trafficking across human brain endothelial cells by Th1- and Th2-polarized lymphocytes. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2004;63:223–232. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
