To do or not to do: the neural signature of self-control
- PMID: 17715350
- PMCID: PMC6672190
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0924-07.2007
To do or not to do: the neural signature of self-control
Abstract
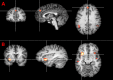
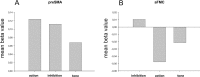
Voluntary action is fundamental to human existence. Recent research suggests that volition involves a specific network of brain activity, centered on the fronto-median cortex. An important but neglected aspect of intentional action involves the decision whether to act or not. This decision process is crucial in daily life because it allows us to form intentions without necessarily implementing them. In the present study, we investigate the neural correlates of intentionally inhibiting actions using functional magnetic resonance imaging. Our data show that a specific area of the fronto-median cortex is more strongly activated when people prepare manual actions but then intentionally cancel them, compared with when they prepare and then complete the same actions. Our results suggest that the human brain network for intentional action includes a control structure for self-initiated inhibition or withholding of intended actions. The mental control of action has an enduring scientific interest, linked to the philosophical concept of "free will." Our results identify a candidate brain area that reflects the crucial decision to do or not to do.
Figures
Comment in
-
Endogenous inhibition and the neural basis of "free won't".J Neurosci. 2007 Dec 19;27(51):13919-20. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4943-07.2007. J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 18094228 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- Abler B, Walter H, Erk S. Neural correlates of frustration. NeuroReport. 2005;16:669–672. - PubMed
-
- Aron AR, Fletcher PC, Bullmore ET, Sahakian BJ, Robbins TW. Stop-signal inhibition disrupted by damage to right inferior frontal gyrus in humans. Nat Neurosci. 2003;6:115–116. - PubMed
-
- Ball T, Schreiber A, Feige B, Wagner M, Lucking CH, Kristeva-Feige R. The role of higher-order motor areas in voluntary movement as revealed by high-resolution EEG and fMRI. NeuroImage. 1999;10:682–694. - PubMed
-
- Baumeister RF, Exline JJ. Virtue, personality, and social relations: self-control as the moral muscle. J Pers. 1999;67:1165–1194. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
