Histatin 5 initiates osmotic stress response in Candida albicans via activation of the Hog1 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway
- PMID: 17715369
- PMCID: PMC2043398
- DOI: 10.1128/EC.00039-07
Histatin 5 initiates osmotic stress response in Candida albicans via activation of the Hog1 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway
Abstract
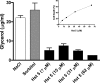
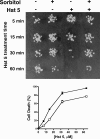
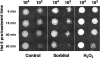
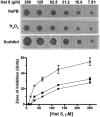
Histatin 5 (Hst 5) is a salivary cationic peptide that has toxicity for Candida albicans by inducing rapid cellular ion imbalance and cell volume loss. Microarray analyses of peptide-treated cells were used to evaluate global gene responses elicited by Hst 5. The major transcriptional response of C. albicans to Hst 5 was expression of genes involved in adaptation to osmotic stress, including production of glycerol (RHR2, SKO1, and PDC11) and the general stress response (CTA1 and HSP70). The oxidative-stress genes AHP1, TRX1, and GPX1 were mildly induced by Hst 5. Cell defense against Hst 5 was dependent on the Hog1 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway, since C. albicans hog1/hog1 mutants were significantly hypersensitive to Hst 5 but not to Mkc1 MAPK or Cek1 MAPK mutants. Activation of the high-osmolarity glycerol (HOG) pathway was demonstrated by phosphorylation of Hog1 MAPK as well as by glycerol production following Hst 5 treatment in a dose-dependent manner. C. albicans cells prestressed with sorbitol were less sensitive to subsequent Hst 5 treatment; however, cells treated concurrently with osmotic stress and Hst 5 were hypersensitive to Hst 5. In contrast, cells subjected to oxidative stress had no difference in sensitivity to Hst 5. These results suggest a common underlying cellular response to osmotic stress and Hst 5. The HOG stress response pathway likely represents a significant and effective challenge to physiological levels of Hst 5 and other toxic peptides in fungal cells.
Figures
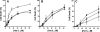

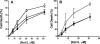

Similar articles
-
Candida albicans Cek1 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling enhances fungicidal activity of salivary histatin 5.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015;59(6):3460-8. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00214-15. Epub 2015 Mar 30. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015. PMID: 25824232 Free PMC article.
-
Non-canonical Activities of Hog1 Control Sensitivity of Candida albicans to Killer Toxins From Debaryomyces hansenii.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018 May 3;8:135. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2018.00135. eCollection 2018. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29774204 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the Hog1 stress-activated protein kinase in the global transcriptional response to stress in the fungal pathogen Candida albicans.Mol Biol Cell. 2006 Feb;17(2):1018-32. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e05-06-0501. Epub 2005 Dec 7. Mol Biol Cell. 2006. PMID: 16339080 Free PMC article.
-
The role of MAPK signal transduction pathways in the response to oxidative stress in the fungal pathogen Candida albicans: implications in virulence.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2010 Dec;11(8):693-703. doi: 10.2174/138920310794557655. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2010. PMID: 21235505 Review.
-
How does it kill?: understanding the candidacidal mechanism of salivary histatin 5.Eukaryot Cell. 2014 Aug;13(8):958-64. doi: 10.1128/EC.00095-14. Epub 2014 Jun 20. Eukaryot Cell. 2014. PMID: 24951439 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Candida albicans Cek1 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling enhances fungicidal activity of salivary histatin 5.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015;59(6):3460-8. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00214-15. Epub 2015 Mar 30. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015. PMID: 25824232 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial Peptides: a New Frontier in Antifungal Therapy.mBio. 2020 Nov 3;11(6):e02123-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02123-20. mBio. 2020. PMID: 33144376 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Blocking two-component signalling enhances Candida albicans virulence and reveals adaptive mechanisms that counteract sustained SAPK activation.PLoS Pathog. 2017 Jan 30;13(1):e1006131. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006131. eCollection 2017 Jan. PLoS Pathog. 2017. PMID: 28135328 Free PMC article.
-
Bcr1 functions downstream of Ssd1 to mediate antimicrobial peptide resistance in Candida albicans.Eukaryot Cell. 2013 Mar;12(3):411-9. doi: 10.1128/EC.00285-12. Epub 2013 Jan 11. Eukaryot Cell. 2013. PMID: 23314964 Free PMC article.
-
Candida albicans flu1-mediated efflux of salivary histatin 5 reduces its cytosolic concentration and fungicidal activity.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013 Apr;57(4):1832-9. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02295-12. Epub 2013 Feb 4. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013. PMID: 23380720 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arana, D. M., C. Nombela, R. Alonso-Monge, and J. Pla. 2005. The Pbs2 MAP kinase kinase is essential for the oxidative stress response in the fungal pathogen Candida albicans. Microbiology 151:1033-1049. - PubMed
-
- Baev, D., A. Rivetta, S. Vylkova, J. N. Sun, G. F. Zeng, C. L. Slayman, and M. Edgerton. 2004. The TRK1 potassium transporter is the critical effector for killing of Candida albicans by the cationic protein, histatin 5. J. Biol. Chem. 279:55060-55072. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

