Bim mediates mitochondria-regulated particulate matter-induced apoptosis in alveolar epithelial cells
- PMID: 17716672
- PMCID: PMC2140150
- DOI: 10.1016/j.febslet.2007.07.080
Bim mediates mitochondria-regulated particulate matter-induced apoptosis in alveolar epithelial cells
Abstract
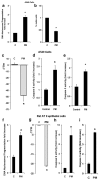
We studied the role of Bim, a pro-apoptotic BCL-2 family member in Airborne particulate matter (PM 2.5 microm)-induced apoptosis in alveolar epithelial cells (AEC). PM induced AEC apoptosis by causing significant reduction of mitochondrial membrane potential and increase in caspase-9, caspase-3 and PARP-1 activation. PM upregulated pro-apoptotic protein Bim and enhanced translocation of Bim to the mitochondria. ShRNABim blocked PM-induced apoptosis by preventing activation of the mitochondrial death pathway suggesting a role of Bim in the regulation of mitochondrial pathway in AEC. Accordingly, we provide the evidence that Bim mediates PM-induced apoptosis via mitochondrial pathway.
Figures

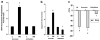

Similar articles
-
BH3-only protein Bim is upregulated and mediates the apoptosis of cardiomyocytes under glucose and oxygen-deprivation conditions.Cell Biol Int. 2015 Mar;39(3):318-25. doi: 10.1002/cbin.10392. Epub 2014 Nov 5. Cell Biol Int. 2015. PMID: 25319047
-
Prometaphase arrest-dependent phosphorylation of Bcl-2 and Bim reduces the association of Bcl-2 with Bak or Bim, provoking Bak activation and mitochondrial apoptosis in nocodazole-treated Jurkat T cells.Apoptosis. 2014 Jan;19(1):224-40. doi: 10.1007/s10495-013-0928-1. Apoptosis. 2014. PMID: 24166139
-
18β-glycyrrhetinic acid induces apoptosis through modulation of Akt/FOXO3a/Bim pathway in human breast cancer MCF-7 cells.J Cell Physiol. 2012 May;227(5):1923-31. doi: 10.1002/jcp.22920. J Cell Physiol. 2012. PMID: 21732363
-
Bim(L) displacing Bcl-x(L) promotes Bax translocation during TNFalpha-induced apoptosis.Apoptosis. 2008 Jul;13(7):950-8. doi: 10.1007/s10495-008-0226-5. Epub 2008 May 24. Apoptosis. 2008. PMID: 18500555
-
Bim and the pro-survival Bcl-2 proteins: opposites attract, ERK repels.Cell Cycle. 2007 Sep 15;6(18):2236-40. doi: 10.4161/cc.6.18.4728. Epub 2007 Jul 10. Cell Cycle. 2007. PMID: 17881896 Review.
Cited by
-
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon components contribute to the mitochondria-antiapoptotic effect of fine particulate matter on human bronchial epithelial cells via the aryl hydrocarbon receptor.Part Fibre Toxicol. 2010 Jul 21;7:18. doi: 10.1186/1743-8977-7-18. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2010. PMID: 20663163 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative stress and cell cycle arrest induced by short-term exposure to dustfall PM2.5 in A549 cells.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018 Aug;25(23):22408-22419. doi: 10.1007/s11356-017-0430-3. Epub 2017 Nov 2. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018. PMID: 29098582
-
Cardiac and mitochondrial dysfunction following acute pulmonary exposure to mountaintop removal mining particulate matter.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015 Dec 15;309(12):H2017-30. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00353.2015. Epub 2015 Oct 23. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26497962 Free PMC article.
-
Health and cellular impacts of air pollutants: from cytoprotection to cytotoxicity.Biochem Res Int. 2012;2012:493894. doi: 10.1155/2012/493894. Epub 2012 Apr 9. Biochem Res Int. 2012. PMID: 22550588 Free PMC article.
-
Lung injury after cigarette smoking is particle related.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2011;6:191-8. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S14911. Epub 2011 Mar 10. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2011. PMID: 21660296 Free PMC article.
References
-
- U.N. Environment Program and WHO Report. Air pollution in the world’s megacities: a report from the U.N. Environment Programme and WHO. Environment. 1994;36:5–37.
-
- Prahalad AK, Inmon J, Dailey LA, Madden MC, Ghio AJ, Gallagher JE. Air pollution particles mediated oxidative DNA base damage in a cell free system and in human airway epithelial cells in relation to particulate metal content and bioreactivity. Chem Res Toxicol. 2001;14:879–887. - PubMed
-
- Upadhyay D, Panduri V, Ghio A, Kamp DW. Particulate matter induces alveolar epithelial cell DNA damage and apoptosis: role of free radicals and the mitochondria. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2003;29:180–187. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

