Effects of a common human gene variant of extracellular superoxide dismutase on endothelial function after endotoxin in mice
- PMID: 17717013
- PMCID: PMC2277153
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.140830
Effects of a common human gene variant of extracellular superoxide dismutase on endothelial function after endotoxin in mice
Abstract
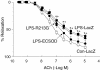
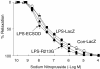
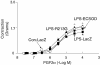
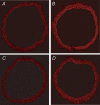
A common gene variant in the heparin-binding domain (HBD) of extracellular superoxide dismutase (ECSOD) may predispose human carriers to ischaemic heart disease. We have demonstrated that the HBD of ECSOD is important for ECSOD to restore vascular dysfunction produced by endotoxin. The purpose of this study was to determine whether the gene variant in the HBD of ECSOD (ECSOD(R213G)) protects against endothelial dysfunction in a model of inflammation. We constructed a recombinant adenovirus that expresses ECSOD(R213G). Adenoviral vectors expressing ECSOD, ECSOD(R213G) or beta-galactosidase (LacZ, a control) were injected i.v. in mice. After 3 days, at which time the plasma SOD activity is maximal, vehicle or endotoxin (lipopolysaccharide or LPS, 40 mg kg(-1)) was injected i.p. Vasomotor function of aorta in vitro was examined 1 day later. Maximal relaxation to sodium nitroprusside was similar in aorta from normal and LPS-treated mice. Maximal relaxation to acetylcholine (10(-5)) was impaired after LPS and LacZ (63 +/- 3%, mean +/- s.e.m.) compared to normal vessels (83 +/- 3%) (P < 0.05). Gene transfer of ECSOD improved (P < 0.05) relaxation in response to acetylcholine (76 +/- 5%) after LPS, whereas gene transfer of ECSOD(R213G) had no effect (65 +/- 4%). Superoxide was increased in aorta (measured using lucigenin and hydroethidine) after LPS, and levels of superoxide were significantly reduced following ECSOD but not ECSOD(R213G). Thus, ECSOD reduces superoxide and improves relaxation to acetylcholine in the aorta after LPS, while the ECSOD variant R213G had minimal effect. These findings suggest that, in contrast to ECSOD, the common human gene variant of ECSOD fails to protect against endothelial dysfunction produced by an inflammatory stimulus.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Endothelial function in the time of the giants.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2008 Nov;52(5):385-92. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0b013e31818a403b. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 19033817 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gene transfer of extracellular superoxide dismutase improves relaxation of aorta after treatment with endotoxin.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2004 Aug;287(2):H805-11. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00907.2003. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2004. PMID: 15277203
-
Vascular effects of a common gene variant of extracellular superoxide dismutase in heart failure.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2006 Aug;291(2):H914-20. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00080.2006. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16840738
-
Gene transfer of extracellular superoxide dismutase improves endothelial function in rats with heart failure.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2005 Aug;289(2):H525-32. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00108.2005. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2005. PMID: 16014615
-
Extracellular superoxide dismutase (ecSOD) in vascular biology: an update on exogenous gene transfer and endogenous regulators of ecSOD.Transl Res. 2008 Feb;151(2):68-78. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2007.10.003. Epub 2007 Nov 8. Transl Res. 2008. PMID: 18201674 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Protective effect of extracellular superoxide dismutase on endothelial function during aging.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2009 Jun;296(6):H1920-5. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.01342.2008. Epub 2009 Apr 17. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19376805 Free PMC article.
-
Hydroethidine- and MitoSOX-derived red fluorescence is not a reliable indicator of intracellular superoxide formation: another inconvenient truth.Free Radic Biol Med. 2010 Apr 15;48(8):983-1001. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2010.01.028. Epub 2010 Jan 29. Free Radic Biol Med. 2010. PMID: 20116425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of lung oxidative damage by endogenous superoxide dismutase in sepsis.Intensive Care Med Exp. 2014 Dec;2(1):17. doi: 10.1186/2197-425X-2-17. Epub 2014 May 23. Intensive Care Med Exp. 2014. PMID: 26266917 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial function in the time of the giants.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2008 Nov;52(5):385-92. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0b013e31818a403b. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 19033817 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathologic properties of SOD3 variant R213G in the cardiovascular system through the altered neutrophils function.PLoS One. 2020 Jan 31;15(1):e0227449. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0227449. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32004354 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Biguad M, Julou-Schaeffer G, Parratt JR, Stoclet JC. Endotoxin-induced impairment of vascular smooth muscle contractions elicited by different mechanisms. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990;190:185–192. - PubMed
-
- Boyle WA, 3rd, Parvathaneni LS, Bourlier V, Sauter C, Laubach VE, Cobb JP. iNOS gene expression modulates microvascular responsiveness in endotoxin-challenged mice. Circ Res. 2000;87:E18–E24. - PubMed
-
- Chu Y, Alwahdani A, Iida S, Lund DD, Faraci FM, Heistad DD. Effects of gene variant of extracellular superoxide dismutase in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Circulation. 2005;112:1047–1053. - PubMed
-
- Chu Y, Heistad DD. Gene transfer to blood vessels using adenoviral vectors. Methods Enzymol. 2002;346:263–276. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

